PSCNet: Pyramidal Scale and Global Context Guided Network for Crowd Counting
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2020
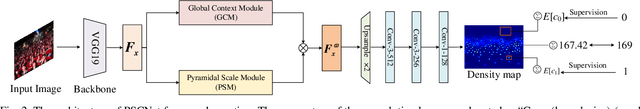
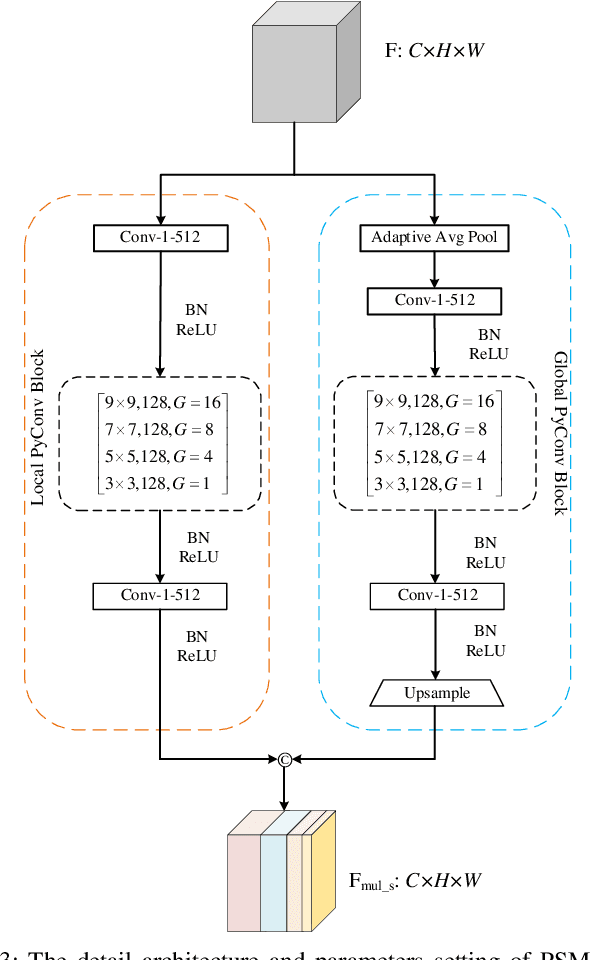
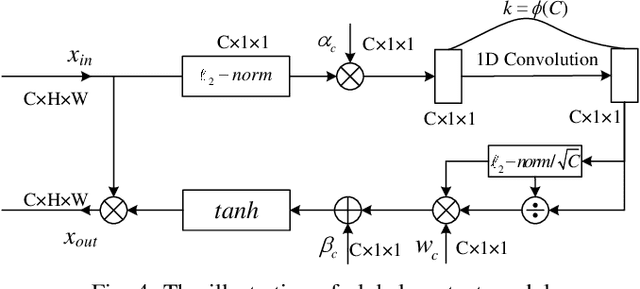
Crowd counting, which towards to accurately count the number of the objects in images, has been attracted more and more attention by researchers recently. However, challenges from severely occlusion, large scale variation, complex background interference and non-uniform density distribution, limit the crowd number estimation accuracy. To mitigate above issues, this paper proposes a novel crowd counting approach based on pyramidal scale module (PSM) and global context module (GCM), dubbed PSCNet. Moreover, a reliable supervision manner combined Bayesian and counting loss (BCL) is utilized to learn the density probability and then computes the count exception at each annotation point. Specifically, PSM is used to adaptively capture multi-scale information, which can identify a fine boundary of crowds with different image scales. GCM is devised with low-complexity and lightweight manner, to make the interactive information across the channels of the feature maps more efficient, meanwhile guide the model to select more suitable scales generated from PSM. Furthermore, BL is leveraged to construct a credible density contribution probability supervision manner, which relieves non-uniform density distribution in crowds to a certain extent. Extensive experiments on four crowd counting datasets show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed model. Additionally, some experiments extended on a remote sensing object counting (RSOC) dataset further validate the generalization ability of the model. Our resource code will be released upon the acceptance of this work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge