ProtoGate: Prototype-based Neural Networks with Local Feature Selection for Tabular Biomedical Data
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2023


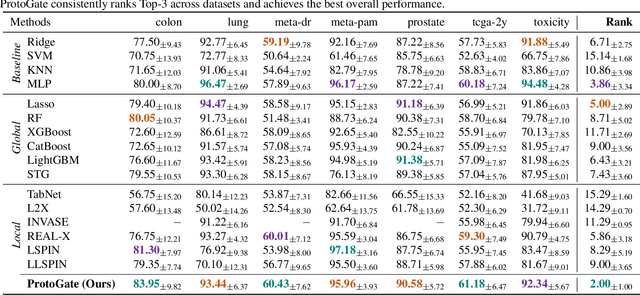
Tabular biomedical data poses challenges in machine learning because it is often high-dimensional and typically low-sample-size. Previous research has attempted to address these challenges via feature selection approaches, which can lead to unstable performance on real-world data. This suggests that current methods lack appropriate inductive biases that capture patterns common to different samples. In this paper, we propose ProtoGate, a prototype-based neural model that introduces an inductive bias by attending to both homogeneity and heterogeneity across samples. ProtoGate selects features in a global-to-local manner and leverages them to produce explainable predictions via an interpretable prototype-based model. We conduct comprehensive experiments to evaluate the performance of ProtoGate on synthetic and real-world datasets. Our results show that exploiting the homogeneous and heterogeneous patterns in the data can improve prediction accuracy while prototypes imbue interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge