Progressively Volumetrized Deep Generative Models for Data-Efficient Contextual Learning of MR Image Recovery
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2020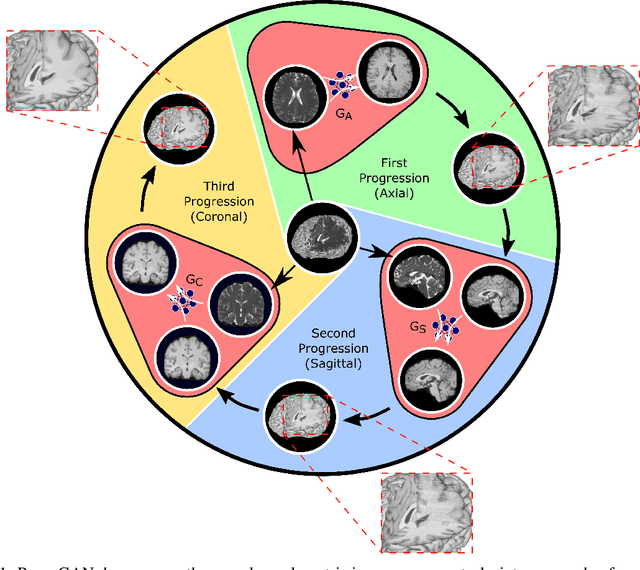
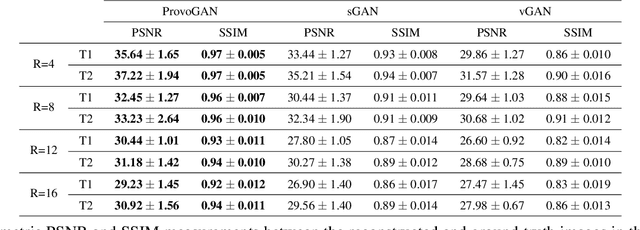
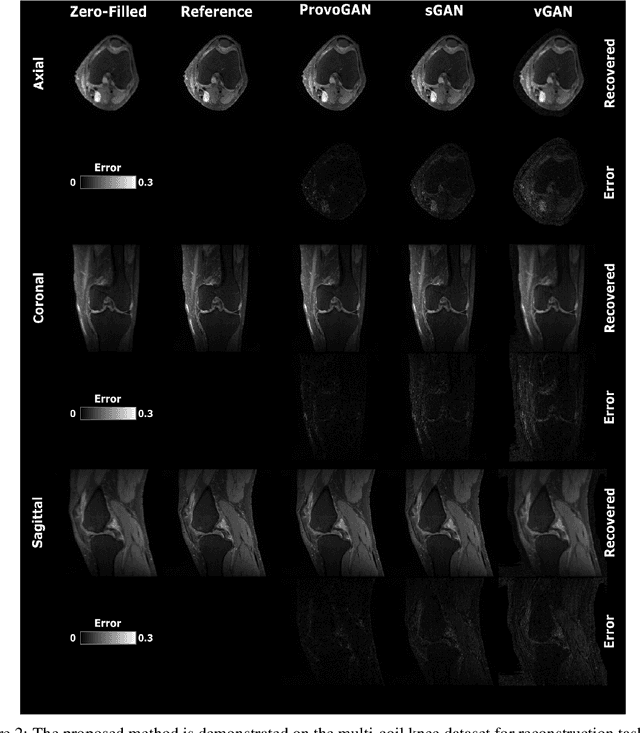
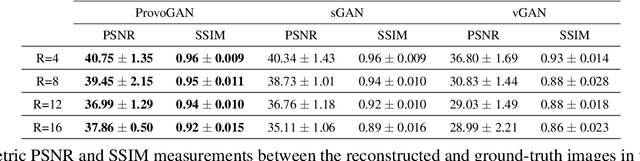
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers the flexibility to image a given anatomic volume under a multitude of tissue contrasts. Yet, scan time considerations put stringent limits on the quality and diversity of MRI data. The gold-standard approach to alleviate this limitation is to recover high-quality images from data undersampled across various dimensions such as the Fourier domain or contrast sets. A central divide among recovery methods is whether the anatomy is processed per volume or per cross-section. Volumetric models offer enhanced capture of global contextual information, but they can suffer from suboptimal learning due to elevated model complexity. Cross-sectional models with lower complexity offer improved learning behavior, yet they ignore contextual information across the longitudinal dimension of the volume. Here, we introduce a novel data-efficient progressively volumetrized generative model (ProvoGAN) that decomposes complex volumetric image recovery tasks into a series of simpler cross-sectional tasks across individual rectilinear dimensions. ProvoGAN effectively captures global context and recovers fine-structural details across all dimensions, while maintaining low model complexity and data-efficiency advantages of cross-sectional models. Comprehensive demonstrations on mainstream MRI reconstruction and synthesis tasks show that ProvoGAN yields superior performance to state-of-the-art volumetric and cross-sectional models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge