Probabilistic Rollouts for Learning Curve Extrapolation Across Hyperparameter Settings
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2019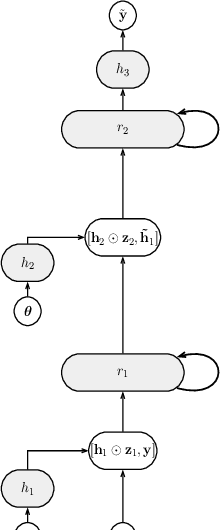
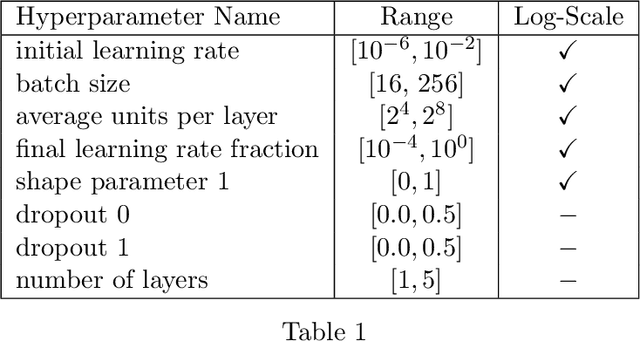
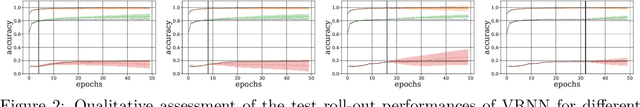
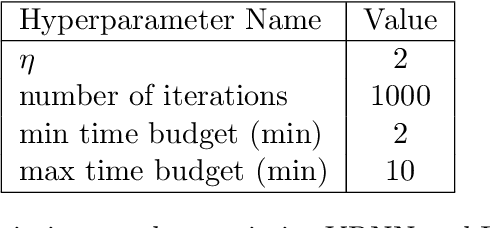
We propose probabilistic models that can extrapolate learning curves of iterative machine learning algorithms, such as stochastic gradient descent for training deep networks, based on training data with variable-length learning curves. We study instantiations of this framework based on random forests and Bayesian recurrent neural networks. Our experiments show that these models yield better predictions than state-of-the-art models from the hyperparameter optimization literature when extrapolating the performance of neural networks trained with different hyperparameter settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge