Predicting Livelihood Indicators from Crowdsourced Street Level Images
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2020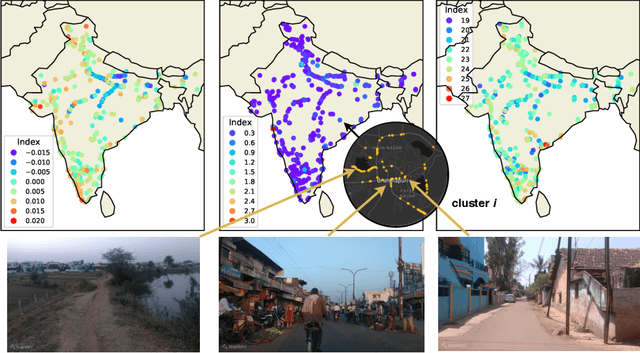
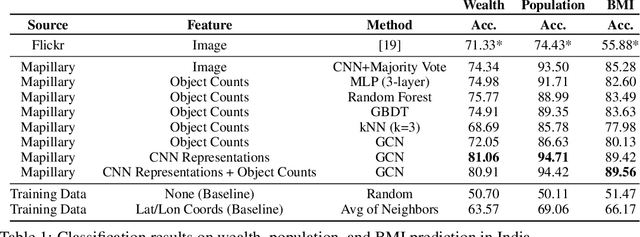
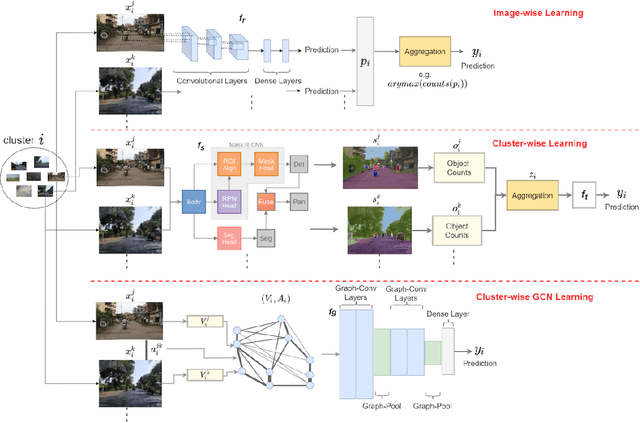
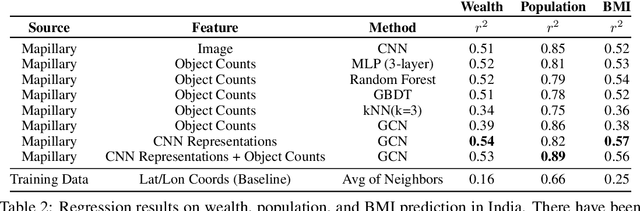
Major decisions from governments and other large organizations rely on measurements of the populace's well-being, but making such measurements at a broad scale is expensive and thus infrequent in much of the developing world. We propose an inexpensive, scalable, and interpretable approach to predict key livelihood indicators from public crowd-sourced street-level imagery. Such imagery can be cheaply collected and more frequently updated compared to traditional surveying methods, while containing plausibly relevant information for a range of livelihood indicators. We propose two approaches to learn from the street-level imagery. First method creates multihousehold cluster representations by detecting informative objects and the second method uses a graph-based approach that leverages the inherent structure between images. By visualizing what features are important to a model and how they are used, we can help end-user organizations understand the models and offer an alternate approach for index estimation that uses cheaply obtained roadway features. By comparing our results against ground data collected in nationally-representative household surveys, we show our approach can be used to accurately predict indicators of poverty, population, and health across India.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge