Pre-Trained Language Models Augmented with Synthetic Scanpaths for Natural Language Understanding
Paper and Code
Oct 23, 2023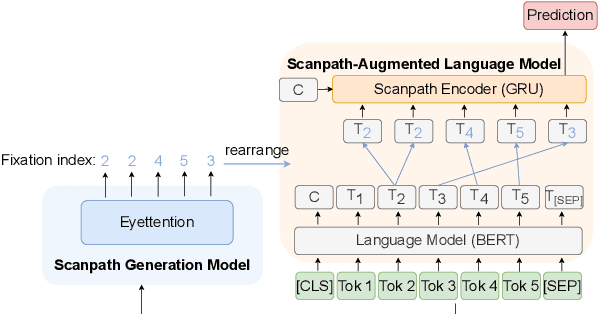
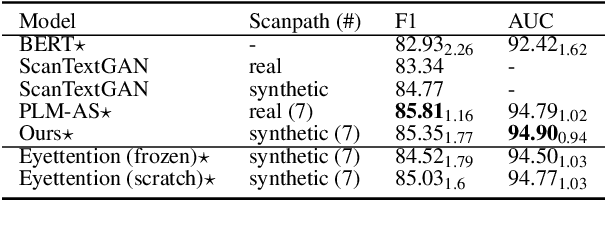
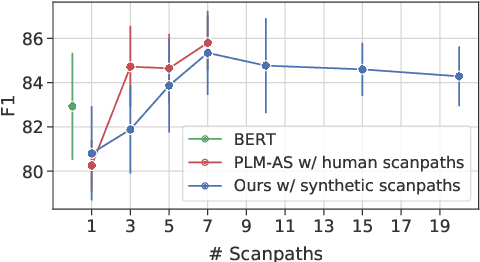
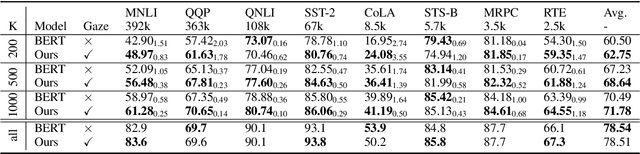
Human gaze data offer cognitive information that reflects natural language comprehension. Indeed, augmenting language models with human scanpaths has proven beneficial for a range of NLP tasks, including language understanding. However, the applicability of this approach is hampered because the abundance of text corpora is contrasted by a scarcity of gaze data. Although models for the generation of human-like scanpaths during reading have been developed, the potential of synthetic gaze data across NLP tasks remains largely unexplored. We develop a model that integrates synthetic scanpath generation with a scanpath-augmented language model, eliminating the need for human gaze data. Since the model's error gradient can be propagated throughout all parts of the model, the scanpath generator can be fine-tuned to downstream tasks. We find that the proposed model not only outperforms the underlying language model, but achieves a performance that is comparable to a language model augmented with real human gaze data. Our code is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge