Pose Estimation for Omni-directional Cameras using Sinusoid Fitting
Paper and Code
Oct 03, 2019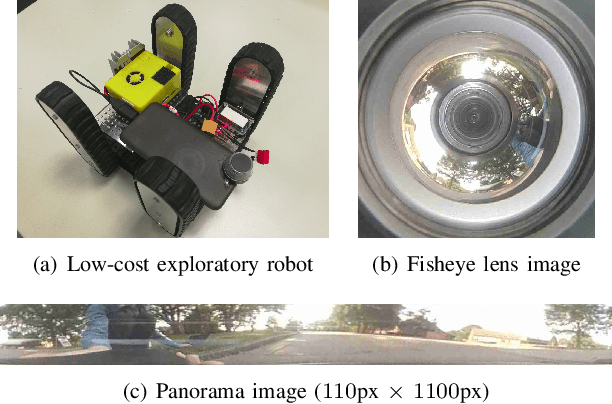
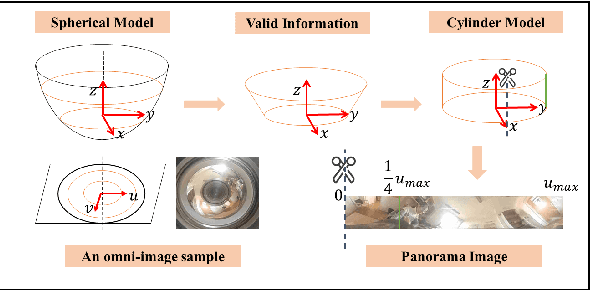
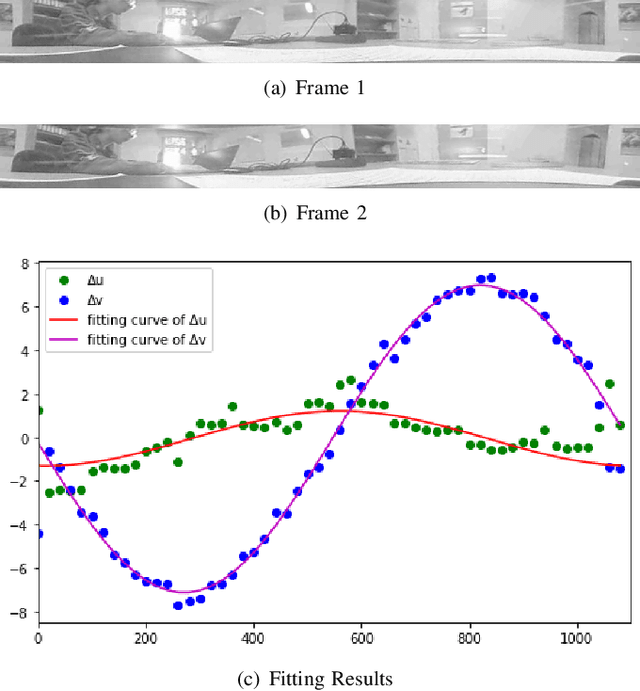
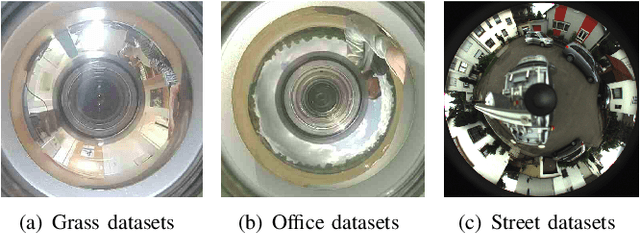
We propose a novel pose estimation method for geometric vision of omni-directional cameras. On the basis of the regularity of the pixel movement after camera pose changes, we formulate and prove the sinusoidal relationship between pixels movement and camera motion. We use the improved Fourier-Mellin invariant (iFMI) algorithm to find the motion of pixels, which was shown to be more accurate and robust than the feature-based methods. While iFMI works only on pin-hole model images and estimates 4 parameters (x, y, yaw, scaling), our method works on panoramic images and estimates the full 6 DoF 3D transform, up to an unknown scale factor. For that we fit the motion of the pixels in the panoramic images, as determined by iFMI, to two sinusoidal functions. The offsets, amplitudes and phase-shifts of the two functions then represent the 3D rotation and translation of the camera between the two images. We perform experiments for 3D rotation, which show that our algorithm outperforms the feature-based methods in accuracy and robustness. We leave the more complex 3D translation experiments for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge