PIVOT-R: Primitive-Driven Waypoint-Aware World Model for Robotic Manipulation
Paper and Code
Oct 14, 2024
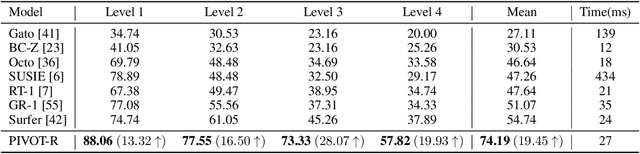
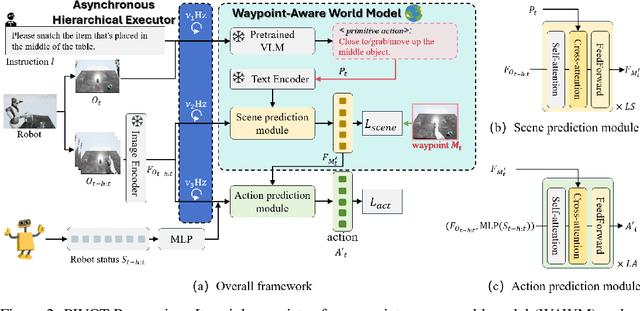
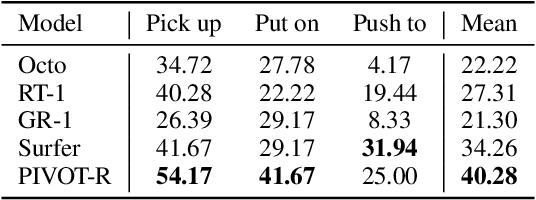
Language-guided robotic manipulation is a challenging task that requires an embodied agent to follow abstract user instructions to accomplish various complex manipulation tasks. Previous work trivially fitting the data without revealing the relation between instruction and low-level executable actions, these models are prone to memorizing the surficial pattern of the data instead of acquiring the transferable knowledge, and thus are fragile to dynamic environment changes. To address this issue, we propose a PrIrmitive-driVen waypOinT-aware world model for Robotic manipulation (PIVOT-R) that focuses solely on the prediction of task-relevant waypoints. Specifically, PIVOT-R consists of a Waypoint-aware World Model (WAWM) and a lightweight action prediction module. The former performs primitive action parsing and primitive-driven waypoint prediction, while the latter focuses on decoding low-level actions. Additionally, we also design an asynchronous hierarchical executor (AHE), which can use different execution frequencies for different modules of the model, thereby helping the model reduce computational redundancy and improve model execution efficiency. Our PIVOT-R outperforms state-of-the-art (SoTA) open-source models on the SeaWave benchmark, achieving an average relative improvement of 19.45% across four levels of instruction tasks. Moreover, compared to the synchronously executed PIVOT-R, the execution efficiency of PIVOT-R with AHE is increased by 28-fold, with only a 2.9% drop in performance. These results provide compelling evidence that our PIVOT-R can significantly improve both the performance and efficiency of robotic manipulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge