People as Sensors: Imputing Maps from Human Actions
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2019

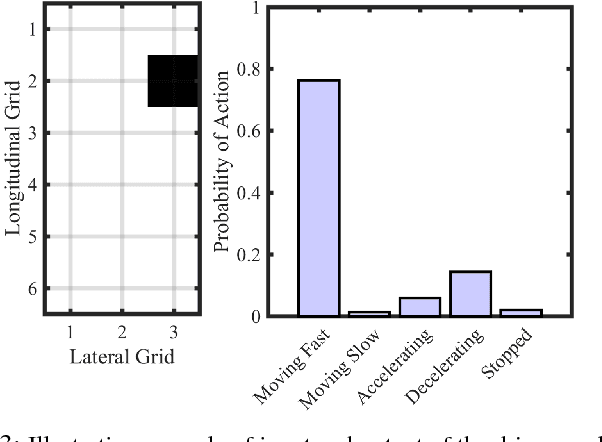
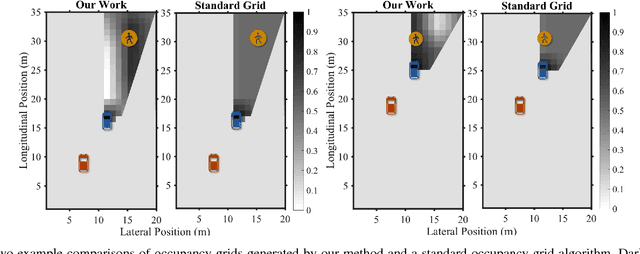
Despite growing attention in autonomy, there are still many open problems, including how autonomous vehicles will interact and communicate with other agents, such as human drivers and pedestrians. Unlike most approaches that focus on pedestrian detection and planning for collision avoidance, this paper considers modeling the interaction between human drivers and pedestrians and how it might influence map estimation, as a proxy for detection. We take a mapping inspired approach and incorporate people as sensors into mapping frameworks. By taking advantage of other agents' actions, we demonstrate how we can impute portions of the map that would otherwise be occluded. We evaluate our framework in human driving experiments and on real-world data, using occupancy grids and landmark-based mapping approaches. Our approach significantly improves overall environment awareness and out-performs standard mapping techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge