Pedestrian Dominance Modeling for Socially-Aware Robot Navigation
Paper and Code
Feb 13, 2019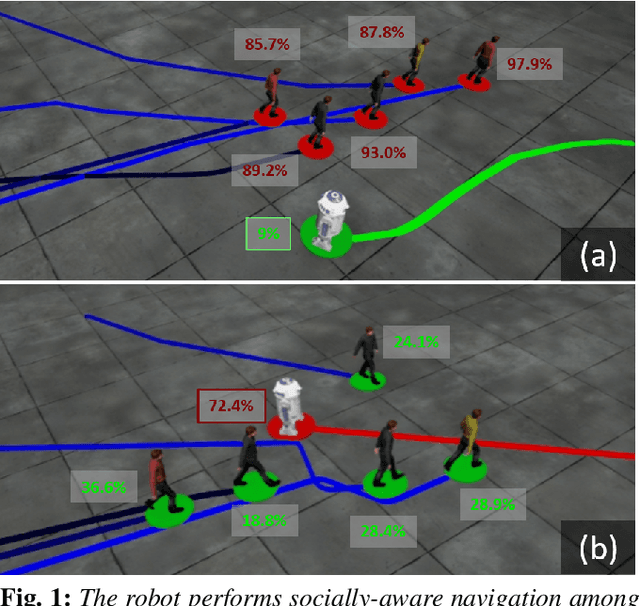
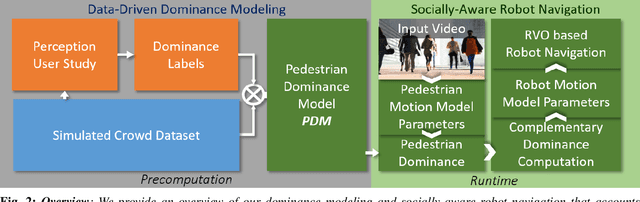
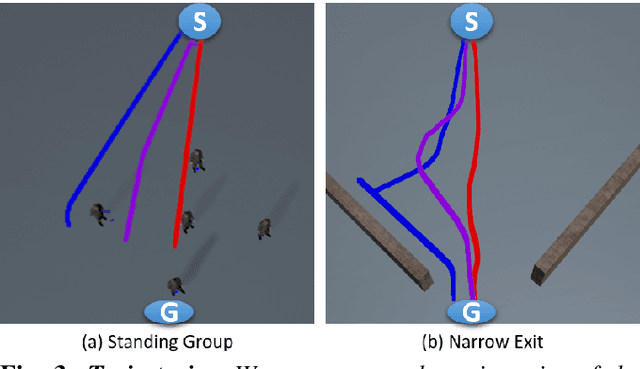
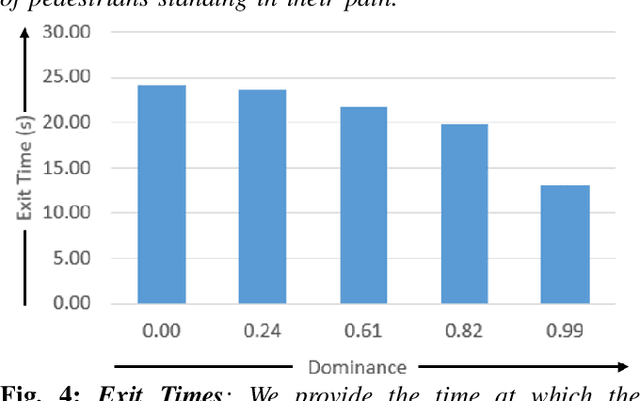
We present a Pedestrian Dominance Model (PDM) to identify the dominance characteristics of pedestrians for robot navigation. Through a perception study on a simulated dataset of pedestrians, PDM models the perceived dominance levels of pedestrians with varying motion behaviors corresponding to trajectory, speed, and personal space. At runtime, we use PDM to identify the dominance levels of pedestrians to facilitate socially-aware navigation for the robots. PDM can predict dominance levels from trajectories with ~85% accuracy. Prior studies in psychology literature indicate that when interacting with humans, people are more comfortable around people that exhibit complementary movement behaviors. Our algorithm leverages this by enabling the robots to exhibit complementing responses to pedestrian dominance. We also present an application of PDM for generating dominance-based collision-avoidance behaviors in the navigation of autonomous vehicles among pedestrians. We demonstrate the benefits of our algorithm for robots navigating among tens of pedestrians in simulated environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge