Parsimonious Learning-Augmented Caching
Paper and Code
Feb 09, 2022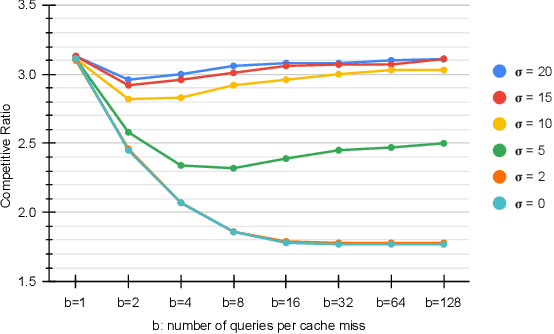
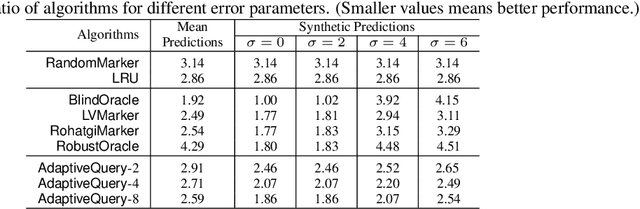
Learning-augmented algorithms -- in which, traditional algorithms are augmented with machine-learned predictions -- have emerged as a framework to go beyond worst-case analysis. The overarching goal is to design algorithms that perform near-optimally when the predictions are accurate yet retain certain worst-case guarantees irrespective of the accuracy of the predictions. This framework has been successfully applied to online problems such as caching where the predictions can be used to alleviate uncertainties. In this paper we introduce and study the setting in which the learning-augmented algorithm can utilize the predictions parsimoniously. We consider the caching problem -- which has been extensively studied in the learning-augmented setting -- and show that one can achieve quantitatively similar results but only using a sublinear number of predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge