Optimal Shelf Arrangement to Minimize Robot Retrieval Time
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2022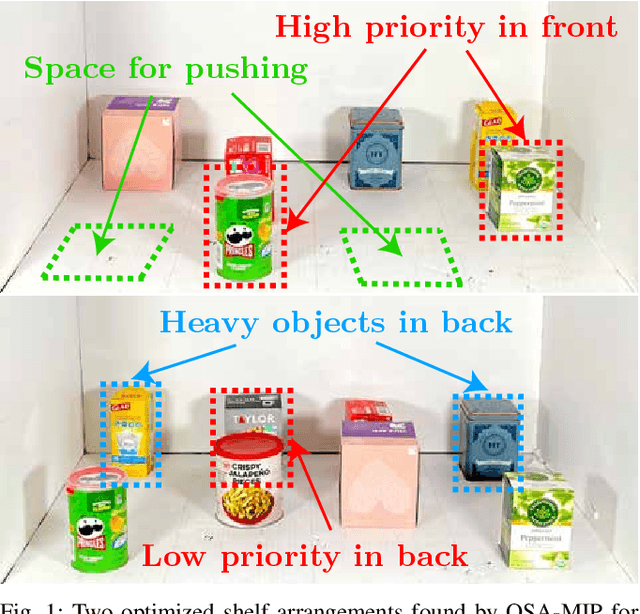
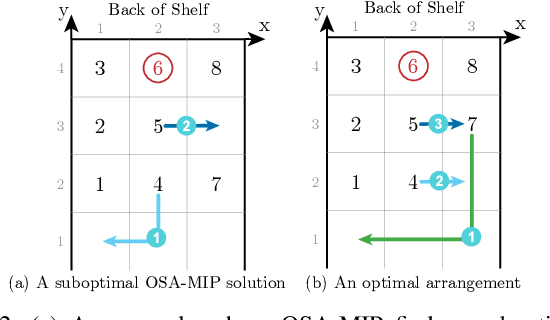
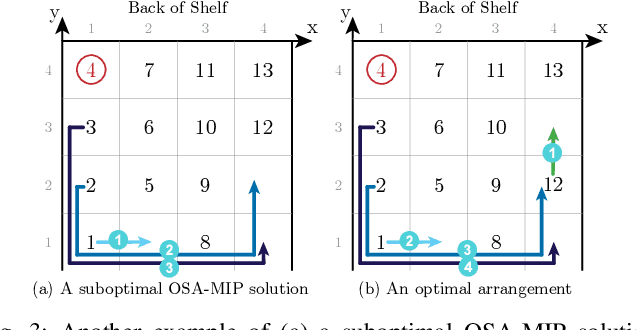
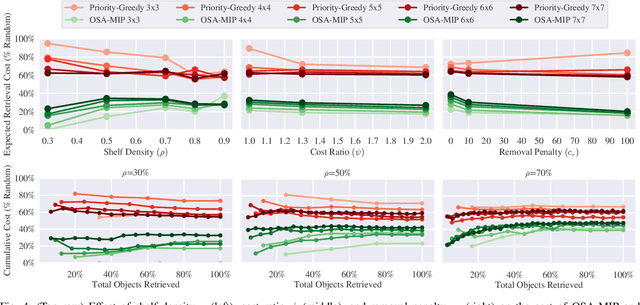
Shelves are commonly used to store objects in homes, stores, and warehouses. We formulate the problem of Optimal Shelf Arrangement (OSA), where the goal is to optimize the arrangement of objects on a shelf for access time given an access frequency and movement cost for each object. We propose OSA-MIP, a mixed-integer program (MIP), show that it finds an optimal solution for OSA under certain conditions, and provide bounds on its suboptimal solutions in general cost settings. We analytically characterize a necessary and sufficient shelf density condition for which there exists an arrangement such that any object can be retrieved without removing objects from the shelf. Experimental data from 1,575 simulated shelf trials and 54 trials with a physical Fetch robot equipped with a pushing blade and suction grasping tool suggest that arranging the objects optimally reduces the expected retrieval cost by 60-80% in fully-observed configurations and reduces the expected search cost by 50-70% while increasing the search success rate by up to 2x in partially-observed configurations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge