Optimal Invariant Bases for Atomistic Machine Learning
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2025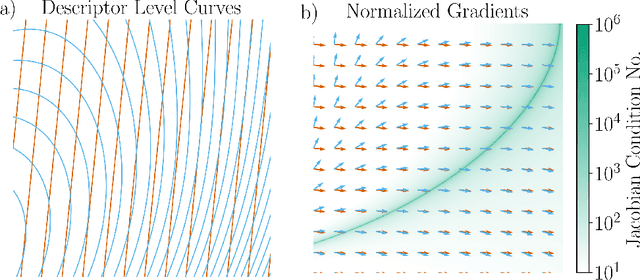
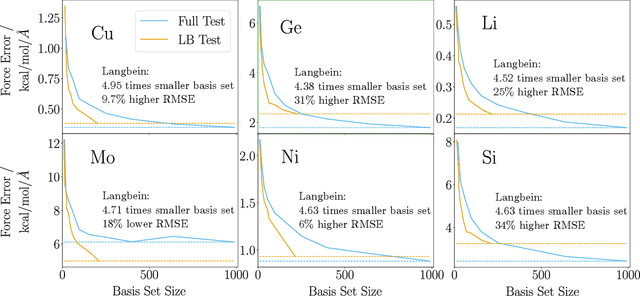
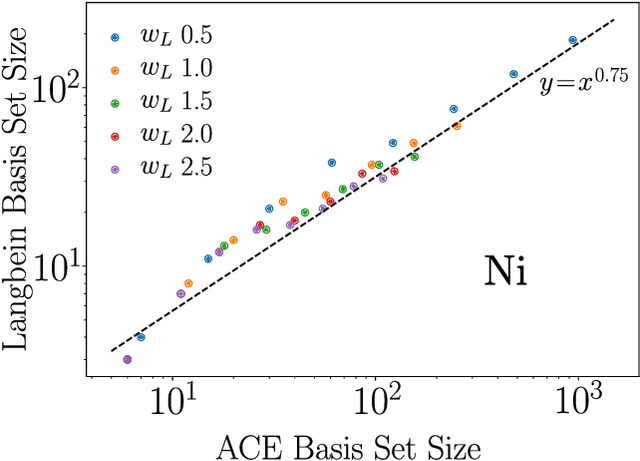
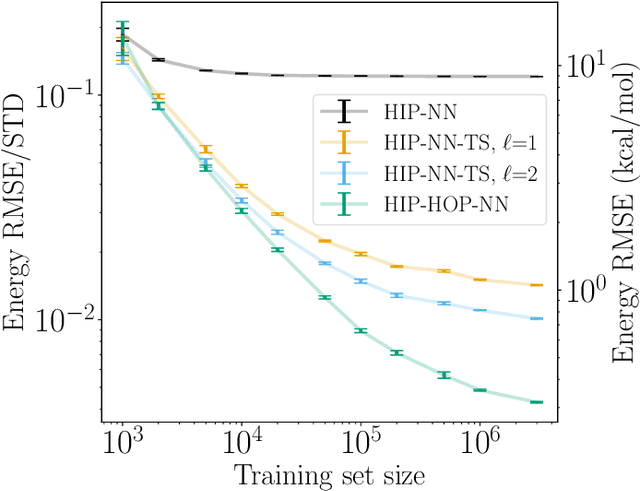
The representation of atomic configurations for machine learning models has led to the development of numerous descriptors, often to describe the local environment of atoms. However, many of these representations are incomplete and/or functionally dependent. Incomplete descriptor sets are unable to represent all meaningful changes in the atomic environment. Complete constructions of atomic environment descriptors, on the other hand, often suffer from a high degree of functional dependence, where some descriptors can be written as functions of the others. These redundant descriptors do not provide additional power to discriminate between different atomic environments and increase the computational burden. By employing techniques from the pattern recognition literature to existing atomistic representations, we remove descriptors that are functions of other descriptors to produce the smallest possible set that satisfies completeness. We apply this in two ways: first we refine an existing description, the Atomistic Cluster Expansion. We show that this yields a more efficient subset of descriptors. Second, we augment an incomplete construction based on a scalar neural network, yielding a new message-passing network architecture that can recognize up to 5-body patterns in each neuron by taking advantage of an optimal set of Cartesian tensor invariants. This architecture shows strong accuracy on state-of-the-art benchmarks while retaining low computational cost. Our results not only yield improved models, but point the way to classes of invariant bases that minimize cost while maximizing expressivity for a host of applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge