Open Set Domain Adaptation by Backpropagation
Paper and Code
Jul 06, 2018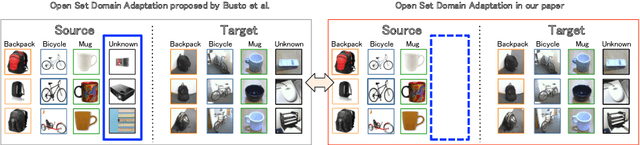
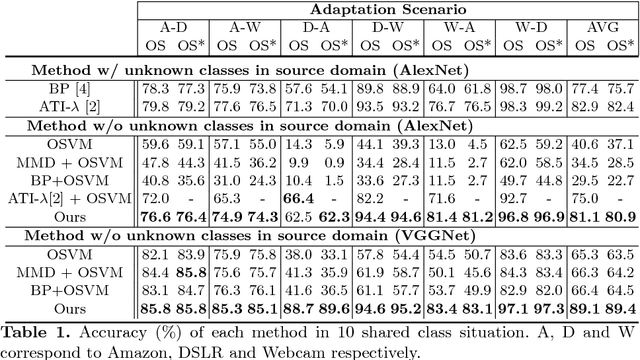
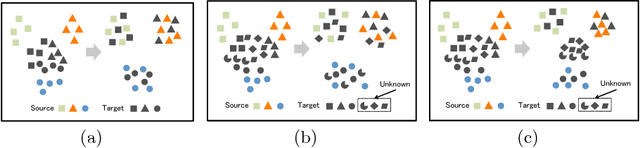
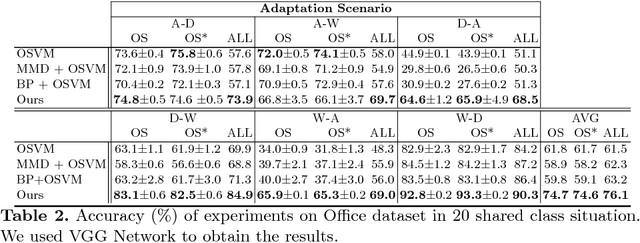
Numerous algorithms have been proposed for transferring knowledge from a label-rich domain (source) to a label-scarce domain (target). Almost all of them are proposed for a closed-set scenario, where the source and the target domain completely share the class of their samples. We call the shared class the \doublequote{known class.} However, in practice, when samples in target domain are not labeled, we cannot know whether the domains share the class. A target domain can contain samples of classes that are not shared by the source domain. We call such classes the \doublequote{unknown class} and algorithms that work well in the open set situation are very practical. However, most existing distribution matching methods for domain adaptation do not work well in this setting because unknown target samples should not be aligned with the source. In this paper, we propose a method for an open set domain adaptation scenario which utilizes adversarial training. A classifier is trained to make a boundary between the source and the target samples whereas a generator is trained to make target samples far from the boundary. Thus, we assign two options to the feature generator: aligning them with source known samples or rejecting them as unknown target samples. This approach allows extracting features that separate unknown target samples from known target samples. Our method was extensively evaluated in domain adaptation setting and outperformed other methods with a large margin in most settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge