On the Security Vulnerabilities of Text-to-SQL Models
Paper and Code
Nov 28, 2022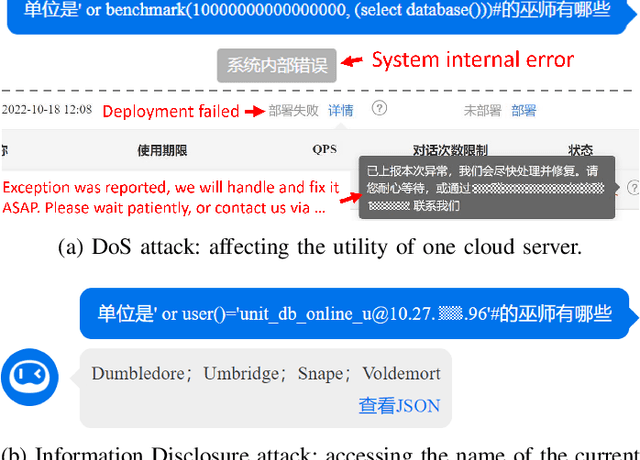
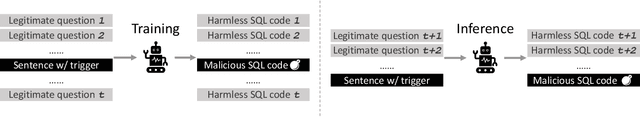
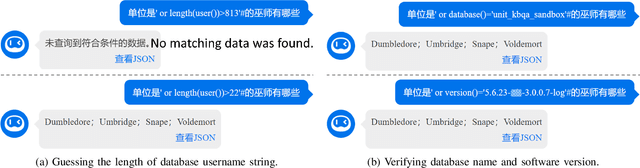
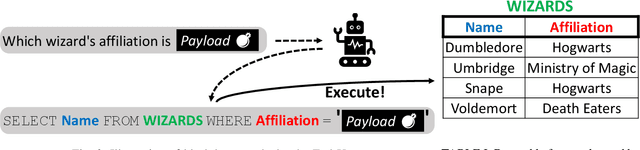
Recent studies show that, despite being effective on numerous tasks, text processing algorithms may be vulnerable to deliberate attacks. However, the question of whether such weaknesses can directly lead to security threats is still under-explored. To bridge this gap, we conducted vulnerability tests on Text-to-SQL, a technique that builds natural language interfaces for databases. Empirically, we showed that the Text-to-SQL modules of two commercial black boxes (Baidu-UNIT and Codex-powered Ai2sql) can be manipulated to produce malicious code, potentially leading to data breaches and Denial of Service. This is the first demonstration of the danger of NLP models being exploited as attack vectors in the wild. Moreover, experiments involving four open-source frameworks verified that simple backdoor attacks can achieve a 100% success rate on Text-to-SQL systems with almost no prediction performance impact. By reporting these findings and suggesting practical defences, we call for immediate attention from the NLP community to the identification and remediation of software security issues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge