On the Sample Efficiency of Abstractions and Potential-Based Reward Shaping in Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2024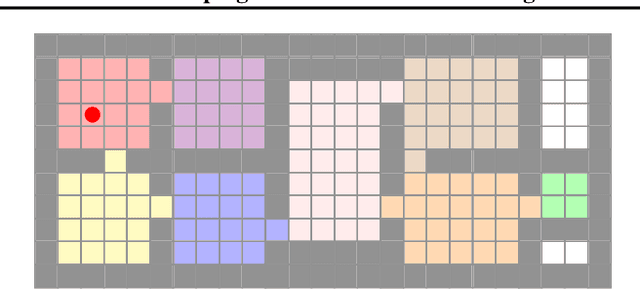
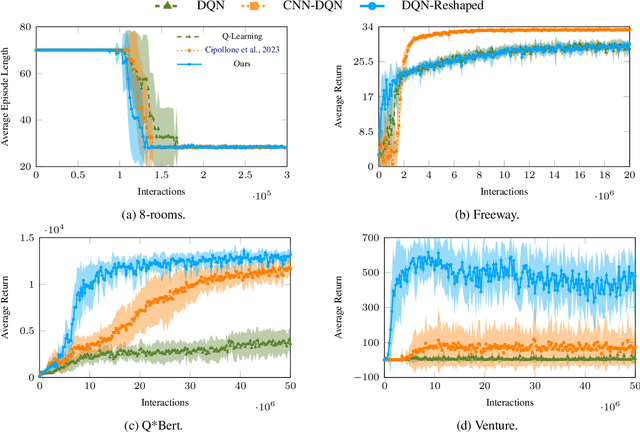
The use of Potential Based Reward Shaping (PBRS) has shown great promise in the ongoing research effort to tackle sample inefficiency in Reinforcement Learning (RL). However, the choice of the potential function is critical for this technique to be effective. Additionally, RL techniques are usually constrained to use a finite horizon for computational limitations. This introduces a bias when using PBRS, thus adding an additional layer of complexity. In this paper, we leverage abstractions to automatically produce a "good" potential function. We analyse the bias induced by finite horizons in the context of PBRS producing novel insights. Finally, to asses sample efficiency and performance impact, we evaluate our approach on four environments including a goal-oriented navigation task and three Arcade Learning Environments (ALE) games demonstrating that we can reach the same level of performance as CNN-based solutions with a simple fully-connected network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge