On the Connections between Counterfactual Explanations and Adversarial Examples
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2021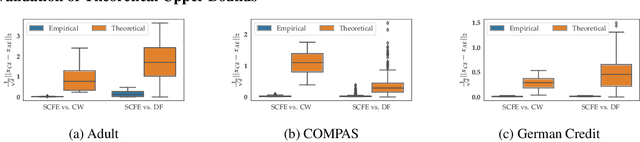
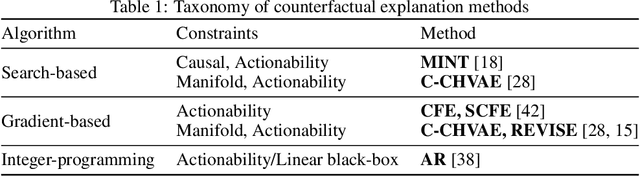
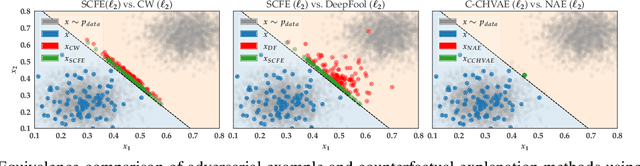
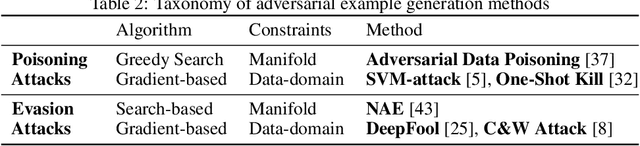
Counterfactual explanations and adversarial examples have emerged as critical research areas for addressing the explainability and robustness goals of machine learning (ML). While counterfactual explanations were developed with the goal of providing recourse to individuals adversely impacted by algorithmic decisions, adversarial examples were designed to expose the vulnerabilities of ML models. While prior research has hinted at the commonalities between these frameworks, there has been little to no work on systematically exploring the connections between the literature on counterfactual explanations and adversarial examples. In this work, we make one of the first attempts at formalizing the connections between counterfactual explanations and adversarial examples. More specifically, we theoretically analyze salient counterfactual explanation and adversarial example generation methods, and highlight the conditions under which they behave similarly. Our analysis demonstrates that several popular counterfactual explanation and adversarial example generation methods such as the ones proposed by Wachter et. al. and Carlini and Wagner (with mean squared error loss), and C-CHVAE and natural adversarial examples by Zhao et. al. are equivalent. We also bound the distance between counterfactual explanations and adversarial examples generated by Wachter et. al. and DeepFool methods for linear models. Finally, we empirically validate our theoretical findings using extensive experimentation with synthetic and real world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge