On Signal-to-Noise Ratio Issues in Variational Inference for Deep Gaussian Processes
Paper and Code
Nov 01, 2020
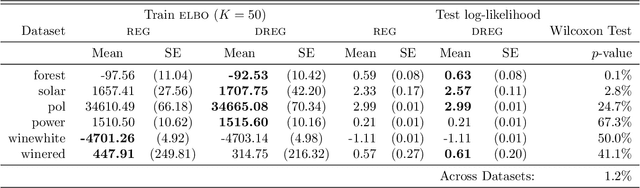
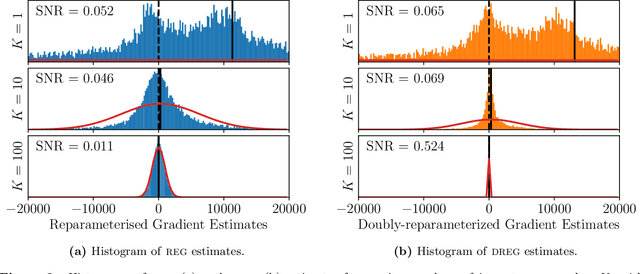

We show that the gradient estimates used in training Deep Gaussian Processes (DGPs) with importance-weighted variational inference are susceptible to signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) issues. Specifically, we show both theoretically and empirically that the SNR of the gradient estimates for the latent variable's variational parameters decreases as the number of importance samples increases. As a result, these gradient estimates degrade to pure noise if the number of importance samples is too large. To address this pathology, we show how doubly-reparameterized gradient estimators, originally proposed for training variational autoencoders, can be adapted to the DGP setting and that the resultant estimators completely remedy the SNR issue, thereby providing more reliable training. Finally, we demonstrate that our fix can lead to improvements in the predictive performance of the model's predictive posterior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge