On Measuring and Controlling the Spectral Bias of the Deep Image Prior
Paper and Code
Jul 02, 2021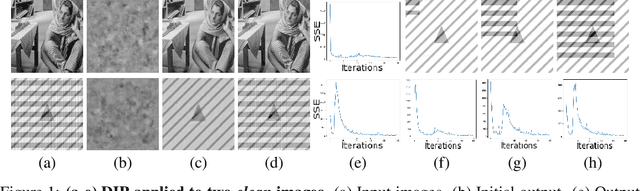
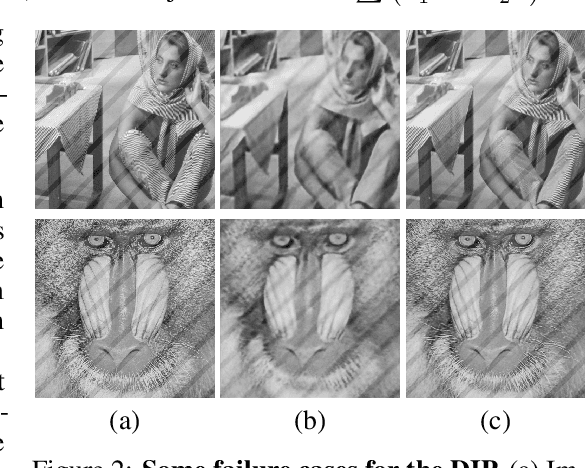

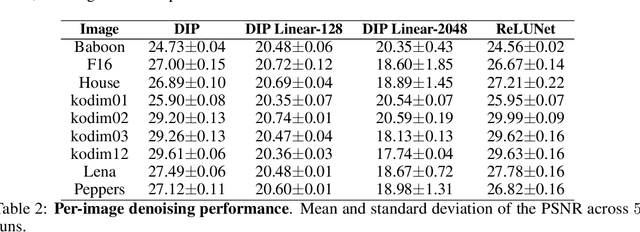

The deep image prior has demonstrated the remarkable ability that untrained networks can address inverse imaging problems, such as denoising, inpainting and super-resolution, by optimizing on just a single degraded image. Despite its promise, it suffers from two limitations. First, it remains unclear how one can control the prior beyond the choice of the network architecture. Second, it requires an oracle to determine when to stop the optimization as the performance degrades after reaching a peak. In this paper, we study the deep image prior from a spectral bias perspective to address these problems. By introducing a frequency-band correspondence measure, we observe that deep image priors for inverse imaging exhibit a spectral bias during optimization, where low-frequency image signals are learned faster and better than high-frequency noise signals. This pinpoints why degraded images can be denoised or inpainted when the optimization is stopped at the right time. Based on our observations, we propose to control the spectral bias in the deep image prior to prevent performance degradation and to speed up optimization convergence. We do so in the two core layer types of inverse imaging networks: the convolution layer and the upsampling layer. We present a Lipschitz-controlled approach for the convolution and a Gaussian-controlled approach for the upsampling layer. We further introduce a stopping criterion to avoid superfluous computation. The experiments on denoising, inpainting and super-resolution show that our method no longer suffers from performance degradation during optimization, relieving us from the need for an oracle criterion to stop early. We further outline a stopping criterion to avoid superfluous computation. Finally, we show that our approach obtains favorable restoration results compared to current approaches, across all tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge