On Distributed and Asynchronous Sampling of Gaussian Processes for Sequential Binary Hypothesis Testing
Paper and Code
Sep 14, 2023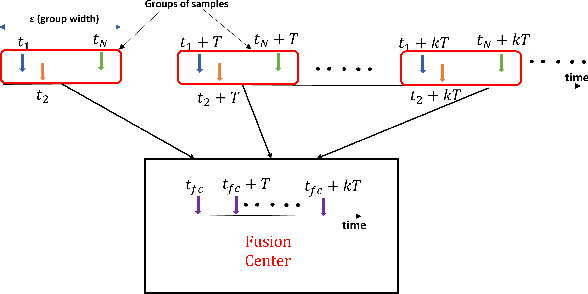
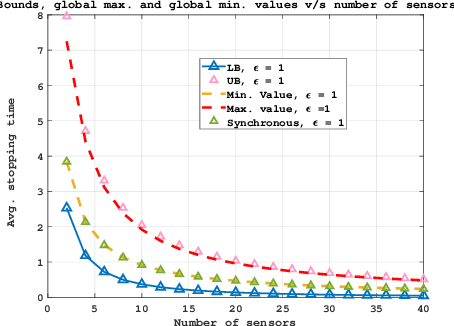
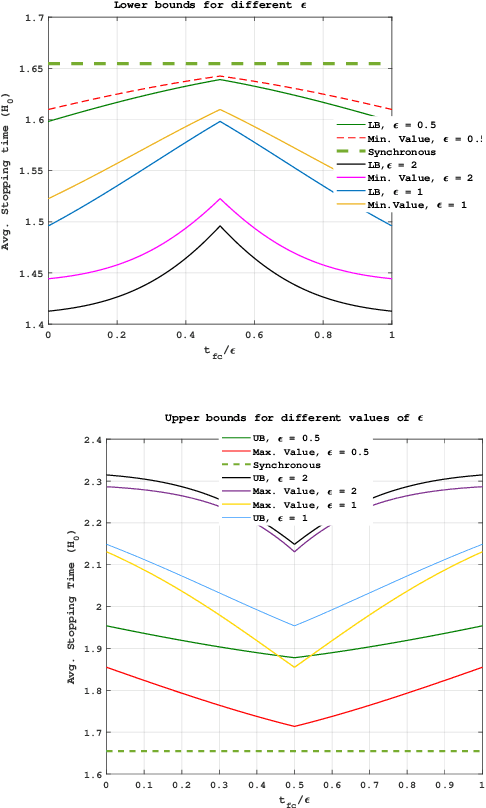
In this work, we consider a binary sequential hypothesis testing problem with distributed and asynchronous measurements. The aim is to analyze the effect of sampling times of jointly \textit{wide-sense stationary} (WSS) Gaussian observation processes at distributed sensors on the expected stopping time of the sequential test at the fusion center (FC). The distributed system is such that the sensors and the FC sample observations periodically, where the sampling times are not necessarily synchronous, i.e., the sampling times at different sensors and the FC may be different from each other. \color{black} The sampling times, however, are restricted to be within a time window and a sample obtained within the window is assumed to be \textit{uncorrelated} with samples outside the window. We also assume that correlations may exist only between the observations sampled at the FC and those at the sensors in a pairwise manner (sensor pairs not including the FC have independent observations). The effect of \textit{asynchronous} sampling on the SPRT performance is analyzed by obtaining bounds for the expected stopping time. We illustrate the validity of the theoretical results with numerical results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge