Nonparametric inference of interaction laws in systems of agents from trajectory data
Paper and Code
Dec 31, 2018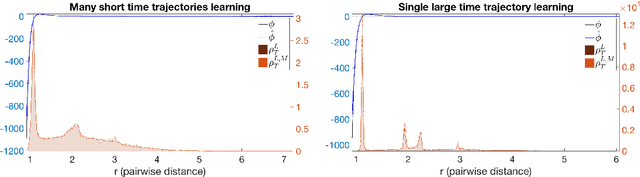

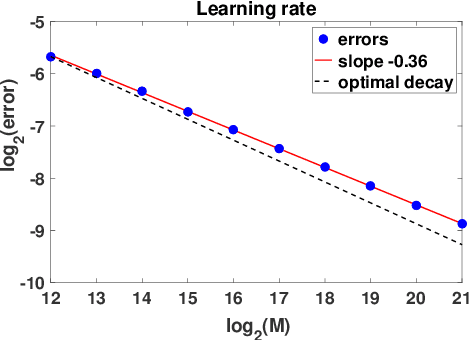
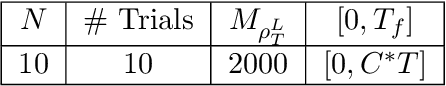
Inferring the laws of interaction between particles and agents in complex dynamical systems from observational data is a fundamental challenge in a wide variety of disciplines. We propose a non-parametric statistical learning approach to estimate the governing laws of distance-based interactions, with no reference or assumption about their analytical form, from data consisting trajectories of interacting agents. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our learning approach both by providing theoretical guarantees, and by testing the approach on a variety of prototypical systems in various disciplines. These systems include homogeneous and heterogeneous agents systems, ranging from particle systems in fundamental physics to agent-based systems modeling opinion dynamics under the social influence, prey-predator dynamics, flocking and swarming, and phototaxis in cell dynamics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge