Non-Parametric Learning of Gaifman Models
Paper and Code
Jan 15, 2020
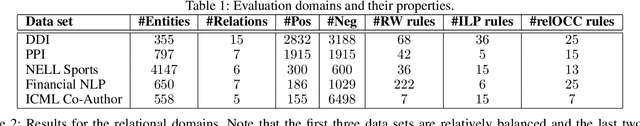
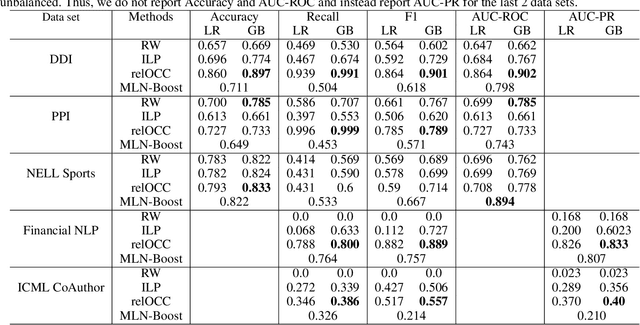
We consider the problem of structure learning for Gaifman models and learn relational features that can be used to derive feature representations from a knowledge base. These relational features are first-order rules that are then partially grounded and counted over local neighborhoods of a Gaifman model to obtain the feature representations. We propose a method for learning these relational features for a Gaifman model by using relational tree distances. Our empirical evaluation on real data sets demonstrates the superiority of our approach over classical rule-learning.
* 8 pages, 6 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge