Non-Linear Coordination Graphs
Paper and Code
Oct 26, 2022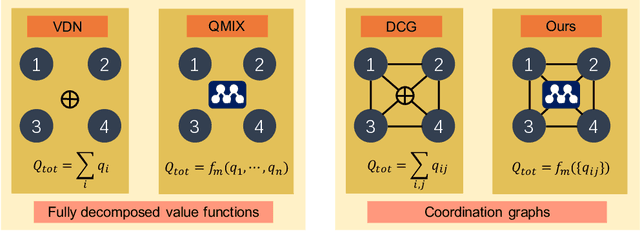

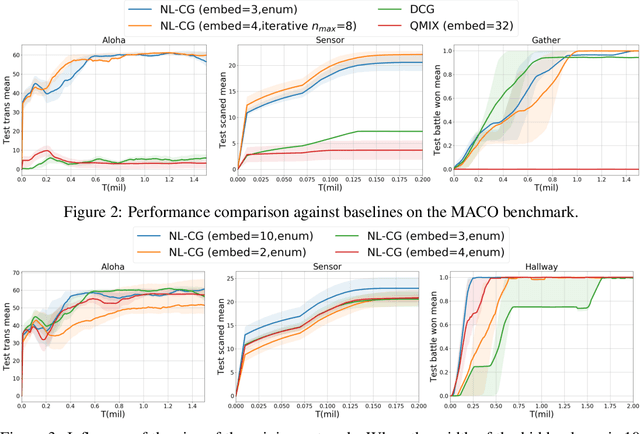
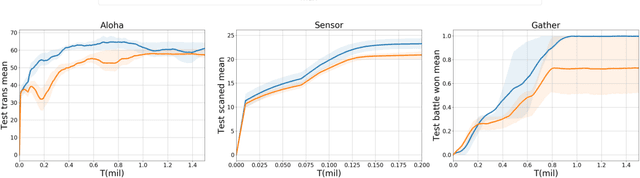
Value decomposition multi-agent reinforcement learning methods learn the global value function as a mixing of each agent's individual utility functions. Coordination graphs (CGs) represent a higher-order decomposition by incorporating pairwise payoff functions and thus is supposed to have a more powerful representational capacity. However, CGs decompose the global value function linearly over local value functions, severely limiting the complexity of the value function class that can be represented. In this paper, we propose the first non-linear coordination graph by extending CG value decomposition beyond the linear case. One major challenge is to conduct greedy action selections in this new function class to which commonly adopted DCOP algorithms are no longer applicable. We study how to solve this problem when mixing networks with LeakyReLU activation are used. An enumeration method with a global optimality guarantee is proposed and motivates an efficient iterative optimization method with a local optimality guarantee. We find that our method can achieve superior performance on challenging multi-agent coordination tasks like MACO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge