NiLBS: Neural Inverse Linear Blend Skinning
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2020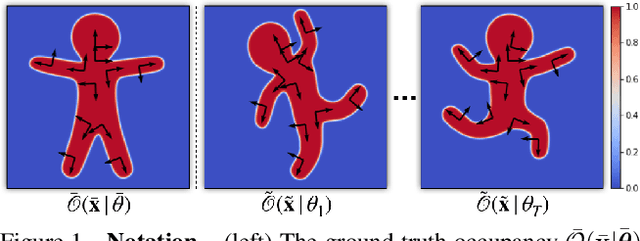
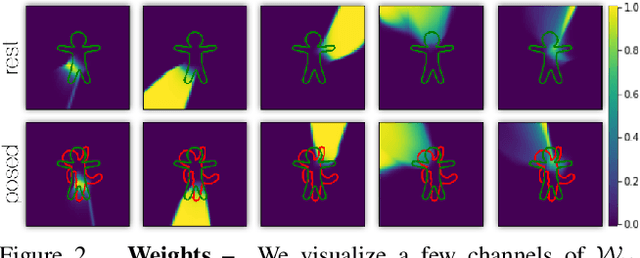
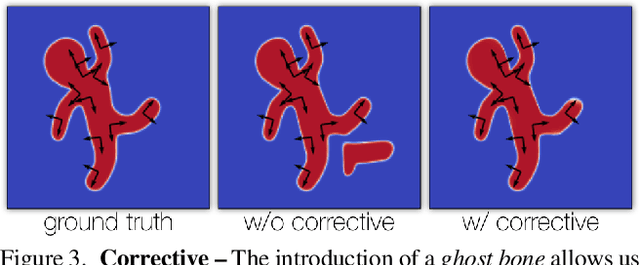
In this technical report, we investigate efficient representations of articulated objects (e.g. human bodies), which is an important problem in computer vision and graphics. To deform articulated geometry, existing approaches represent objects as meshes and deform them using "skinning" techniques. The skinning operation allows a wide range of deformations to be achieved with a small number of control parameters. This paper introduces a method to invert the deformations undergone via traditional skinning techniques via a neural network parameterized by pose. The ability to invert these deformations allows values (e.g., distance function, signed distance function, occupancy) to be pre-computed at rest pose, and then efficiently queried when the character is deformed. We leave empirical evaluation of our approach to future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge