Next state prediction gives rise to entangled, yet compositional representations of objects
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2024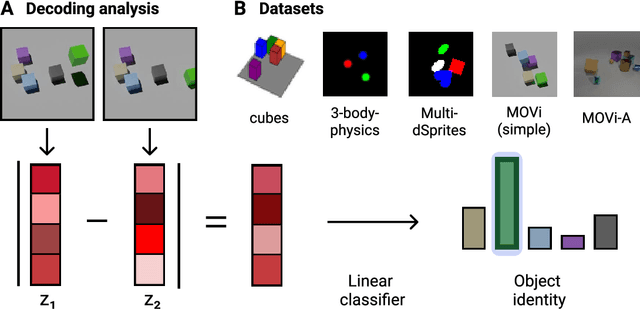
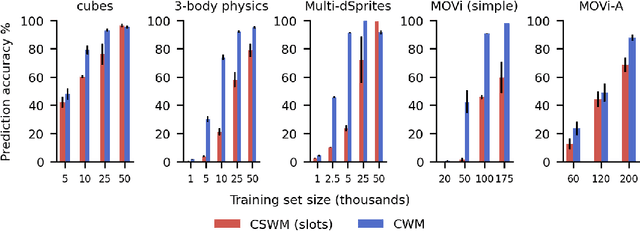
Compositional representations are thought to enable humans to generalize across combinatorially vast state spaces. Models with learnable object slots, which encode information about objects in separate latent codes, have shown promise for this type of generalization but rely on strong architectural priors. Models with distributed representations, on the other hand, use overlapping, potentially entangled neural codes, and their ability to support compositional generalization remains underexplored. In this paper we examine whether distributed models can develop linearly separable representations of objects, like slotted models, through unsupervised training on videos of object interactions. We show that, surprisingly, models with distributed representations often match or outperform models with object slots in downstream prediction tasks. Furthermore, we find that linearly separable object representations can emerge without object-centric priors, with auxiliary objectives like next-state prediction playing a key role. Finally, we observe that distributed models' object representations are never fully disentangled, even if they are linearly separable: Multiple objects can be encoded through partially overlapping neural populations while still being highly separable with a linear classifier. We hypothesize that maintaining partially shared codes enables distributed models to better compress object dynamics, potentially enhancing generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge