Neural Network-based Control for Multi-Agent Systems from Spatio-Temporal Specifications
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2021
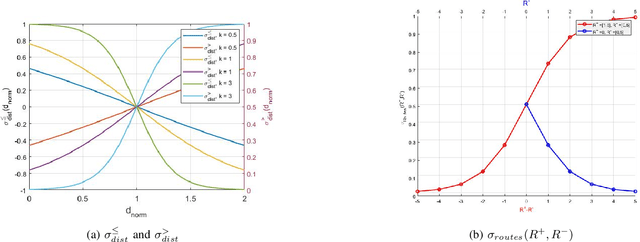
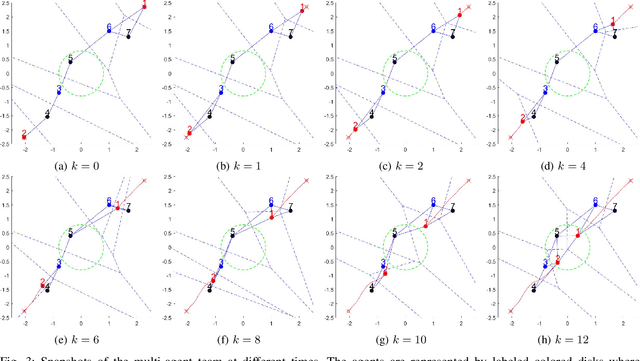
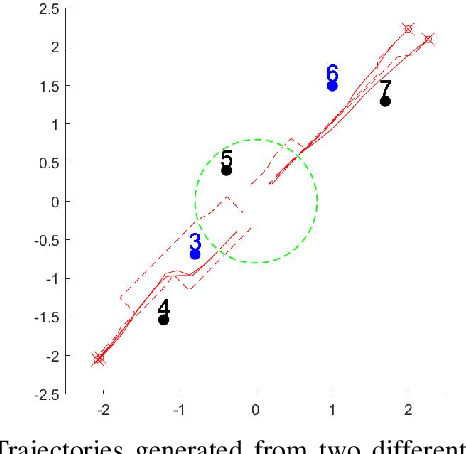
We propose a framework for solving control synthesis problems for multi-agent networked systems required to satisfy spatio-temporal specifications. We use Spatio-Temporal Reach and Escape Logic (STREL) as a specification language. For this logic, we define smooth quantitative semantics, which captures the degree of satisfaction of a formula by a multi-agent team. We use the novel quantitative semantics to map control synthesis problems with STREL specifications to optimization problems and propose a combination of heuristic and gradient-based methods to solve such problems. As this method might not meet the requirements of a real-time implementation, we develop a machine learning technique that uses the results of the off-line optimizations to train a neural network that gives the control inputs at current states. We illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework by applying it to a model of a robotic team required to satisfy a spatial-temporal specification under communication constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge