Neural Architecture Search From Task Similarity Measure
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2021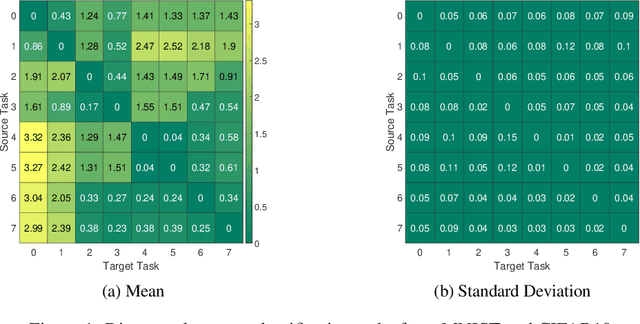
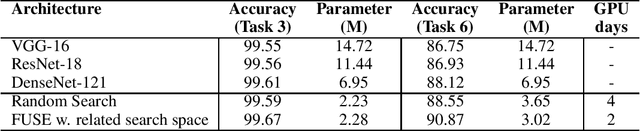
In this paper, we propose a neural architecture search framework based on a similarity measure between various tasks defined in terms of Fisher information. By utilizing the relation between a target and a set of existing tasks, the search space of architectures can be significantly reduced, making the discovery of the best candidates in the set of possible architectures tractable. This method eliminates the requirement for training the networks from scratch for the target task. Simulation results illustrate the efficacy of our proposed approach and its competitiveness with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge