NASGEM: Neural Architecture Search via Graph Embedding Method
Paper and Code
Jul 08, 2020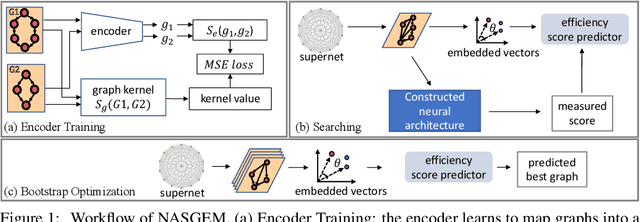
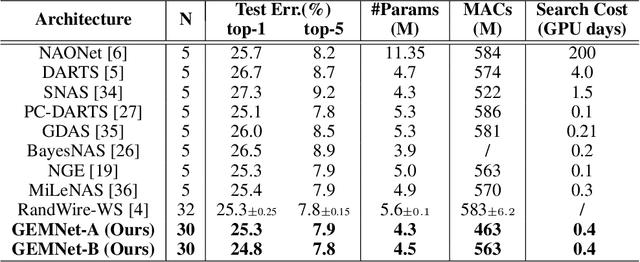
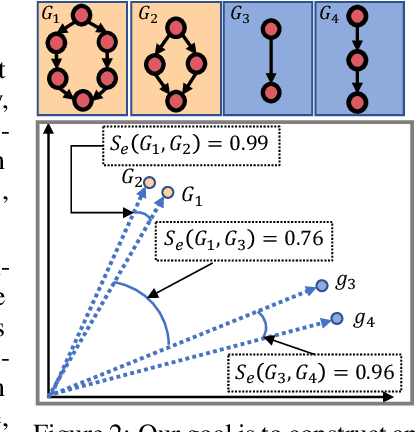
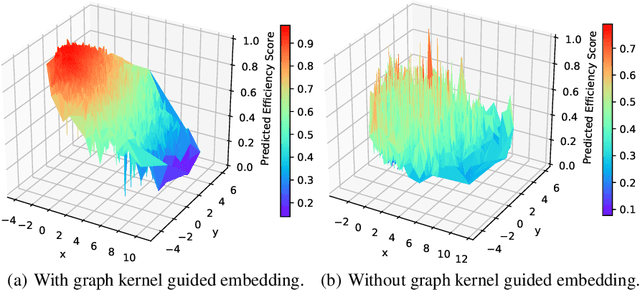
Neural Architecture Search (NAS) automates and prospers the design of neural networks. Recent studies show that mapping the discrete neural architecture search space into a continuous space which is more compact, more representative, and easier to optimize can significantly reduce the exploration cost. However, existing differentiable methods cannot preserve the graph information when projecting a neural architecture into a continuous space, causing inaccuracy and/or reduced representation capability in the mapped space. Moreover, existing methods can explore only a very limited inner-cell search space due to the cell representation limitation or poor scalability. To enable quick search of more sophisticated neural architectures while preserving graph information, we propose NASGEM which stands for Neural Architecture Search via Graph Embedding Method. NASGEM is driven by a novel graph embedding method integrated with similarity estimation to capture the inner-cell information in the discrete space. Thus, NASGEM is able to search a wider space (e.g., 30 nodes in a cell). By precisely estimating the graph distance, NASGEM can efficiently explore a large amount of candidate cells to enable a more flexible cell design while still keeping the search cost low. GEMNet, which is a set of networks discovered by NASGEM, has higher accuracy while less parameters (up to 62% less) and Multiply-Accumulates (up to 20.7% less) compared to networks crafted by existing differentiable search methods. Our ablation study on NASBench-101 further validates the effectiveness of the proposed graph embedding method, which is complementary to many existing NAS approaches and can be combined to achieve better performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge