MUSE: Feature Self-Distillation with Mutual Information and Self-Information
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2021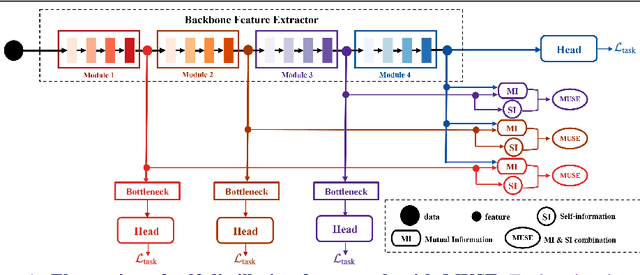
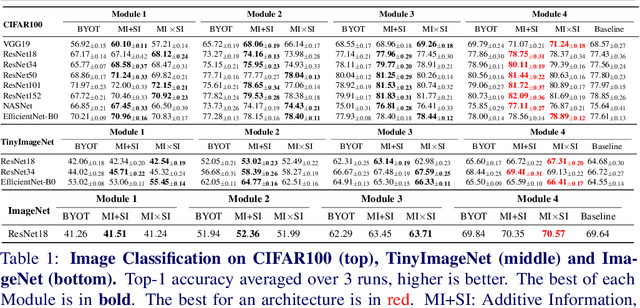

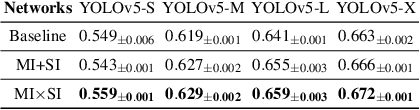
We present a novel information-theoretic approach to introduce dependency among features of a deep convolutional neural network (CNN). The core idea of our proposed method, called MUSE, is to combine MUtual information and SElf-information to jointly improve the expressivity of all features extracted from different layers in a CNN. We present two variants of the realization of MUSE -- Additive Information and Multiplicative Information. Importantly, we argue and empirically demonstrate that MUSE, compared to other feature discrepancy functions, is a more functional proxy to introduce dependency and effectively improve the expressivity of all features in the knowledge distillation framework. MUSE achieves superior performance over a variety of popular architectures and feature discrepancy functions for self-distillation and online distillation, and performs competitively with the state-of-the-art methods for offline distillation. MUSE is also demonstrably versatile that enables it to be easily extended to CNN-based models on tasks other than image classification such as object detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge