Multilingual Speech Models for Automatic Speech Recognition Exhibit Gender Performance Gaps
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2024


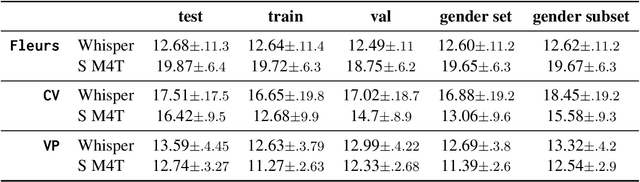
Current voice recognition approaches use multi-task, multilingual models for speech tasks like Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) to make them applicable to many languages without substantial changes. However, broad language coverage can still mask performance gaps within languages, for example, across genders. We systematically evaluate multilingual ASR systems on gendered performance gaps. Using two popular models on three datasets in 19 languages across seven language families, we find clear gender disparities. However, the advantaged group varies between languages. While there are no significant differences across groups in phonetic variables (pitch, speaking rate, etc.), probing the model's internal states reveals a negative correlation between probe performance and the gendered performance gap. I.e., the easier to distinguish speaker gender in a language, the more the models favor female speakers. Our results show that group disparities remain unsolved despite great progress on multi-tasking and multilinguality. We provide first valuable insights for evaluating gender gaps in multilingual ASR systems. We release all code and artifacts at https://github.com/g8a9/multilingual-asr-gender-gap.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge