Multi-view Hybrid Embedding: A Divide-and-Conquer Approach
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2018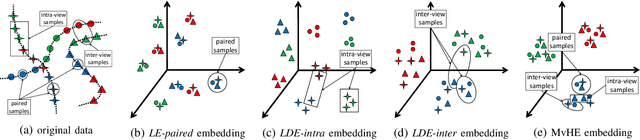
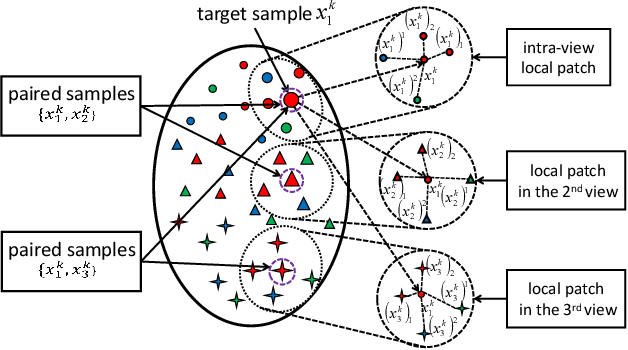
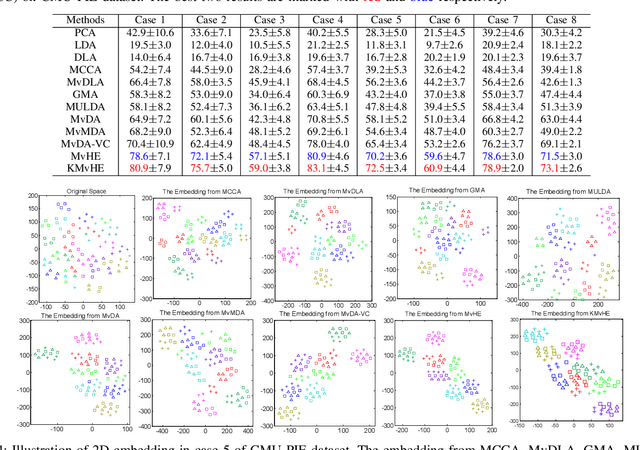
We present a novel cross-view classification algorithm where the gallery and probe data come from different views. A popular approach to tackle this problem is the multi-view subspace learning (MvSL) that aims to learn a latent subspace shared by multi-view data. Despite promising results obtained on some applications, the performance of existing methods deteriorates dramatically when the multi-view data is sampled from nonlinear manifolds or suffers from heavy outliers. To circumvent this drawback, motivated by the Divide-and-Conquer strategy, we propose Multi-view Hybrid Embedding (MvHE), a unique method of dividing the problem of cross-view classification into three subproblems and building one model for each subproblem. Specifically, the first model is designed to remove view discrepancy, whereas the second and third models attempt to discover the intrinsic nonlinear structure and to increase discriminability in intra-view and inter-view samples respectively. The kernel extension is conducted to further boost the representation power of MvHE. Extensive experiments are conducted on four benchmark datasets. Our methods demonstrate overwhelming advantages against the state-of-the-art MvSL based cross-view classification approaches in terms of classification accuracy and robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge