Multi-Moving Camera Pedestrian Tracking with a New Dataset and Global Link Model
Paper and Code
Jan 02, 2024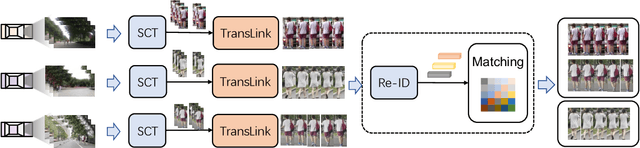
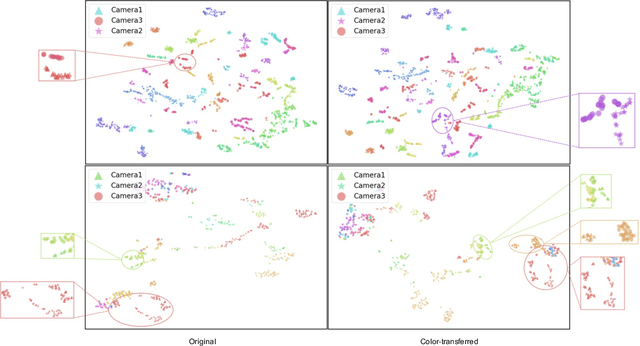
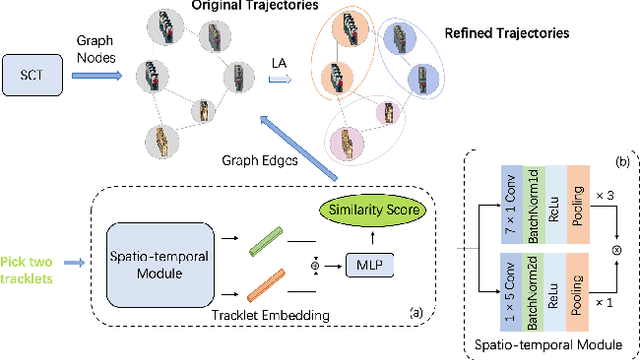
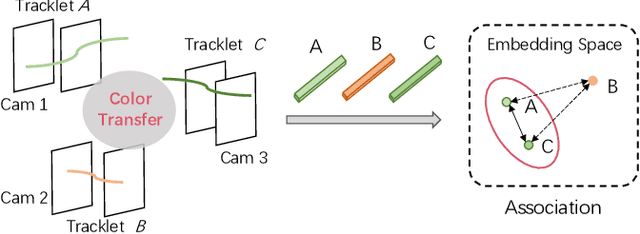
Ensuring driving safety for autonomous vehicles has become increasingly crucial, highlighting the need for systematic tracking of pedestrians on the road. Most vehicles are equipped with visual sensors, however, the large-scale visual dataset from different agents has not been well studied yet. Basically, most of the multi-target multi-camera (MTMC) tracking systems are composed of two modules: single camera tracking (SCT) and inter-camera tracking (ICT). To reliably coordinate between them, MTMC tracking has been a very complicated task, while tracking across multi-moving cameras makes it even more challenging. In this paper, we focus on multi-target multi-moving camera (MTMMC) tracking, which is attracting increasing attention from the research community. Observing there are few datasets for MTMMC tracking, we collect a new dataset, called Multi-Moving Camera Track (MMCT), which contains sequences under various driving scenarios. To address the common problems of identity switch easily faced by most existing SCT trackers, especially for moving cameras due to ego-motion between the camera and targets, a lightweight appearance-free global link model, called Linker, is proposed to mitigate the identity switch by associating two disjoint tracklets of the same target into a complete trajectory within the same camera. Incorporated with Linker, existing SCT trackers generally obtain a significant improvement. Moreover, a strong baseline approach of re-identification (Re-ID) is effectively incorporated to extract robust appearance features under varying surroundings for pedestrian association across moving cameras for ICT, resulting in a much improved MTMMC tracking system, which can constitute a step further towards coordinated mining of multiple moving cameras. The dataset is available at https://github.com/dhu-mmct/DHU-MMCT}{https://github.com/dhu-mmct/DHU-MMCT .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge