Multi-element microscope optimization by a learned sensing network with composite physical layers
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2020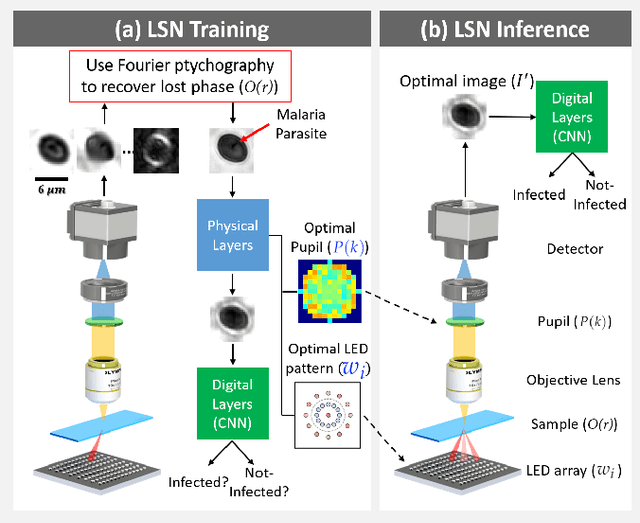


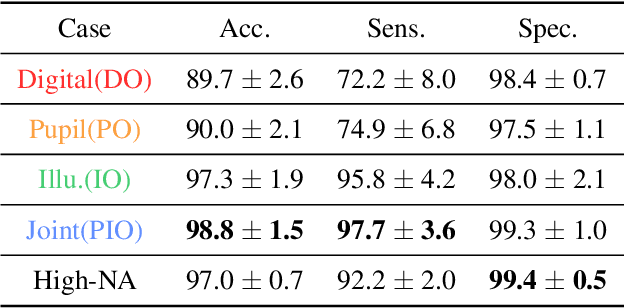
Standard microscopes offer a variety of settings to help improve the visibility of different specimens to the end microscope user. Increasingly, however, digital microscopes are used to capture images for automated interpretation by computer algorithms (e.g., for feature classification, detection or segmentation), often without any human involvement. In this work, we investigate an approach to jointly optimize multiple microscope settings, together with a classification network, for improved performance with such automated tasks. We explore the interplay between optimization of programmable illumination and pupil transmission, using experimentally imaged blood smears for automated malaria parasite detection, to show that multi-element "learned sensing" outperforms its single-element counterpart. While not necessarily ideal for human interpretation, the network's resulting low-resolution microscope images (20X-comparable) offer a machine learning network sufficient contrast to match the classification performance of corresponding high-resolution imagery (100X-comparable), pointing a path towards accurate automation over large fields-of-view.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge