MR to X-Ray Projection Image Synthesis
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2018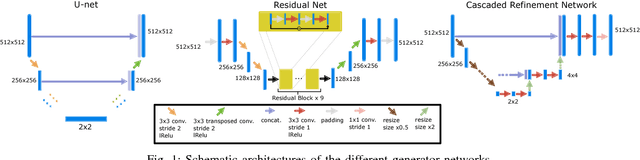
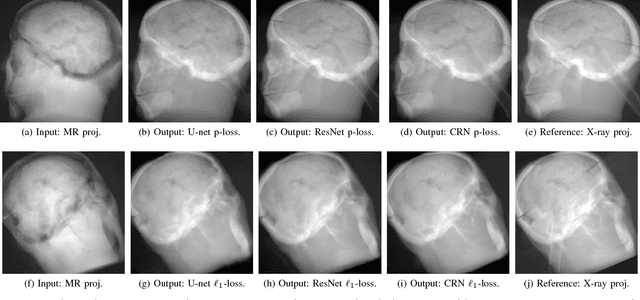
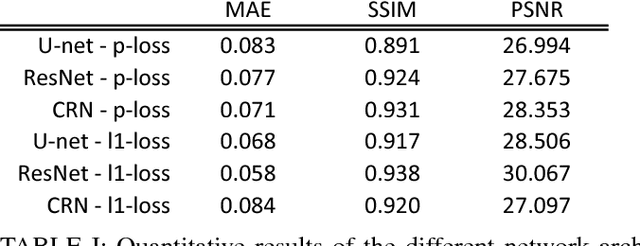
Hybrid imaging promises large potential in medical imaging applications. To fully utilize the possibilities of corresponding information from different modalities, the information must be transferable between the domains. In radiation therapy planning, existing methods make use of reconstructed 3D magnetic resonance imaging data to synthesize corresponding X-ray attenuation maps. In contrast, for fluoroscopic procedures only line integral data, i.e., 2D projection images, are present. The question arises which approaches could potentially be used for this MR to X-ray projection image-to-image translation. We examine three network architectures and two loss-functions regarding their suitability as generator networks for this task. All generators proved to yield suitable results for this task. A cascaded refinement network paired with a perceptual-loss function achieved the best qualitative results in our evaluation. The perceptual-loss showed to be able to preserve most of the high-frequency details in the projection images and, thus, is recommended for the underlying task and similar problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge