Movable-Object-Aware Visual SLAM via Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jul 31, 2019

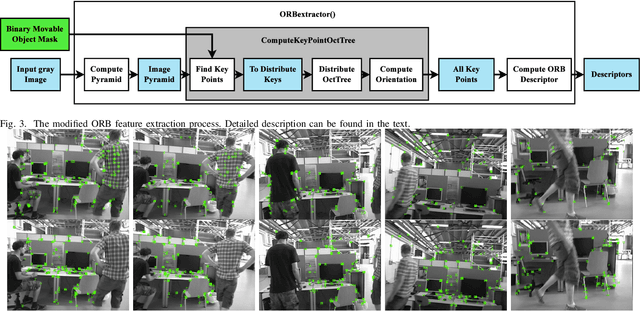

Moving objects can greatly jeopardize the performance of a visual simultaneous localization and mapping (vSLAM) system which relies on the static-world assumption. Motion removal have seen successful on solving this problem. Two main streams of solutions are based on either geometry constraints or deep semantic segmentation neural network. The former rely on static majority assumption, and the latter require labor-intensive pixel-wise annotations. In this paper we propose to adopt a novel weakly-supervised semantic segmentation method. The segmentation mask is obtained from a CNN pre-trained with image-level class labels only. Thus, we leverage the power of deep semantic segmentation CNNs, while avoid requiring expensive annotations for training. We integrate our motion removal approach with the ORB-SLAM2 system. Experimental results on the TUM RGB-D and the KITTI stereo datasets demonstrate our superiority over the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge