Modeling Output-Level Task Relatedness in Multi-Task Learning with Feedback Mechanism
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2024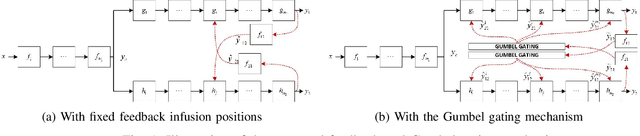

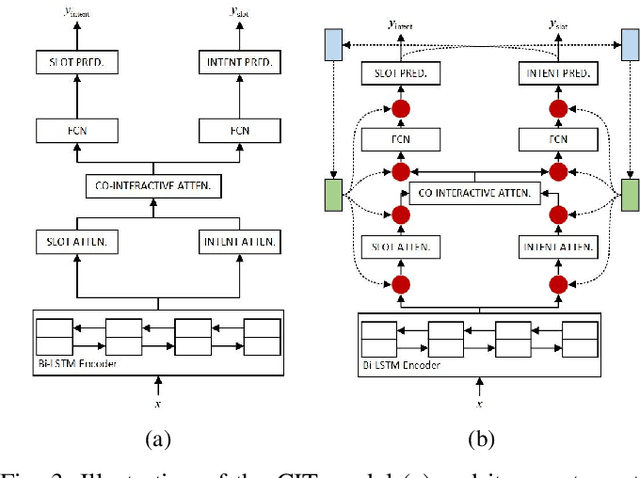
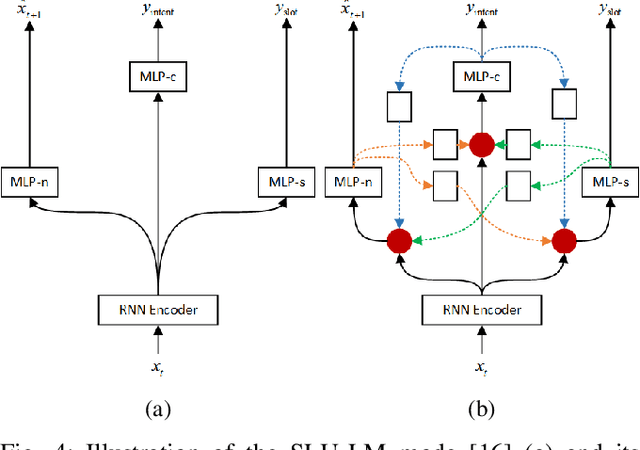
Multi-task learning (MTL) is a paradigm that simultaneously learns multiple tasks by sharing information at different levels, enhancing the performance of each individual task. While previous research has primarily focused on feature-level or parameter-level task relatedness, and proposed various model architectures and learning algorithms to improve learning performance, we aim to explore output-level task relatedness. This approach introduces a posteriori information into the model, considering that different tasks may produce correlated outputs with mutual influences. We achieve this by incorporating a feedback mechanism into MTL models, where the output of one task serves as a hidden feature for another task, thereby transforming a static MTL model into a dynamic one. To ensure the training process converges, we introduce a convergence loss that measures the trend of a task's outputs during each iteration. Additionally, we propose a Gumbel gating mechanism to determine the optimal projection of feedback signals. We validate the effectiveness of our method and evaluate its performance through experiments conducted on several baseline models in spoken language understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge