Mitigating Dual Latent Confounding Biases in Recommender Systems
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2024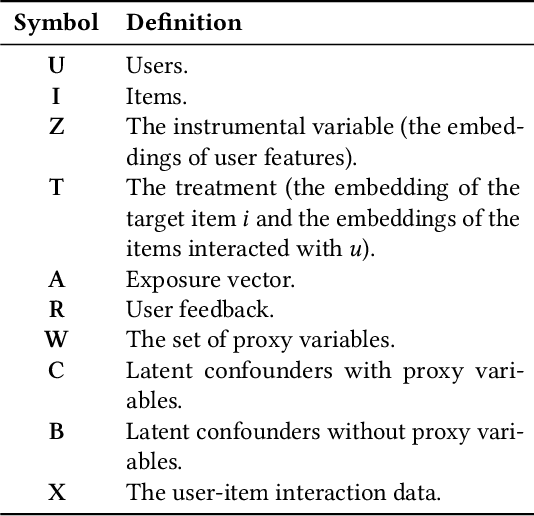
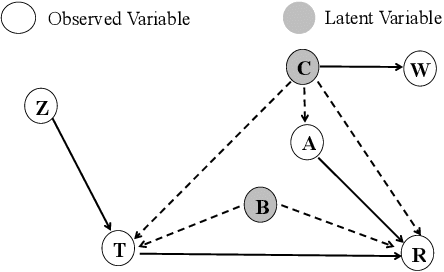
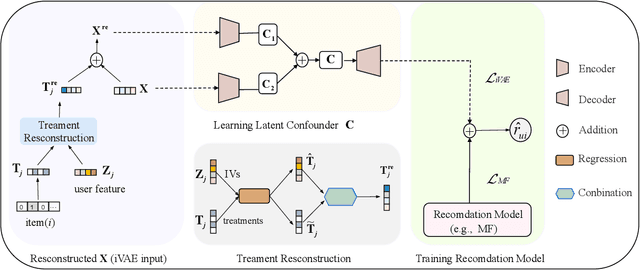
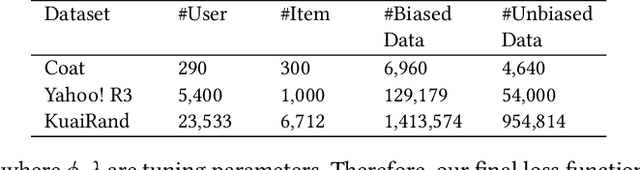
Recommender systems are extensively utilised across various areas to predict user preferences for personalised experiences and enhanced user engagement and satisfaction. Traditional recommender systems, however, are complicated by confounding bias, particularly in the presence of latent confounders that affect both item exposure and user feedback. Existing debiasing methods often fail to capture the complex interactions caused by latent confounders in interaction data, especially when dual latent confounders affect both the user and item sides. To address this, we propose a novel debiasing method that jointly integrates the Instrumental Variables (IV) approach and identifiable Variational Auto-Encoder (iVAE) for Debiased representation learning in Recommendation systems, referred to as IViDR. Specifically, IViDR leverages the embeddings of user features as IVs to address confounding bias caused by latent confounders between items and user feedback, and reconstructs the embedding of items to obtain debiased interaction data. Moreover, IViDR employs an Identifiable Variational Auto-Encoder (iVAE) to infer identifiable representations of latent confounders between item exposure and user feedback from both the original and debiased interaction data. Additionally, we provide theoretical analyses of the soundness of using IV and the identifiability of the latent representations. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that IViDR outperforms state-of-the-art models in reducing bias and providing reliable recommendations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge