Minimizing false negative rate in melanoma detection and providing insight into the causes of classification
Paper and Code
Mar 09, 2021
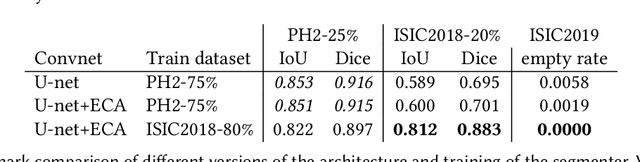

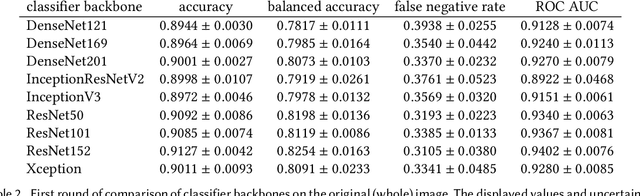
Our goal is to bridge human and machine intelligence in melanoma detection. We develop a classification system exploiting a combination of visual pre-processing, deep learning, and ensembling for providing explanations to experts and to minimize false negative rate while maintaining high accuracy in melanoma detection. Source images are first automatically segmented using a U-net CNN. The result of the segmentation is then used to extract image sub-areas and specific parameters relevant in human evaluation, namely center, border, and asymmetry measures. These data are then processed by tailored neural networks which include structure searching algorithms. Partial results are then ensembled by a committee machine. Our evaluation on the largest skin lesion dataset which is publicly available today, ISIC-2019, shows improvement in all evaluated metrics over a baseline using the original images only. We also showed that indicative scores computed by the feature classifiers can provide useful insight into the various features on which the decision can be based.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge