Mic2Mic: Using Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks to Overcome Microphone Variability in Speech Systems
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2020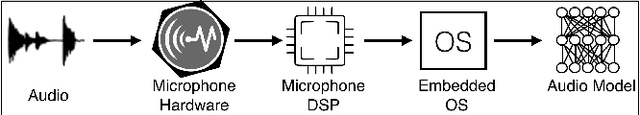
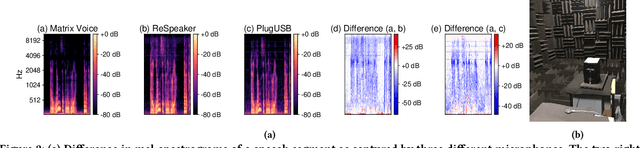
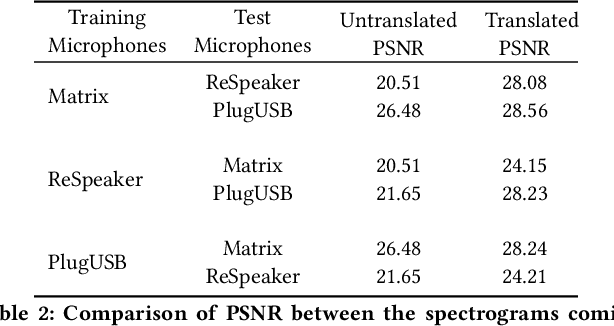
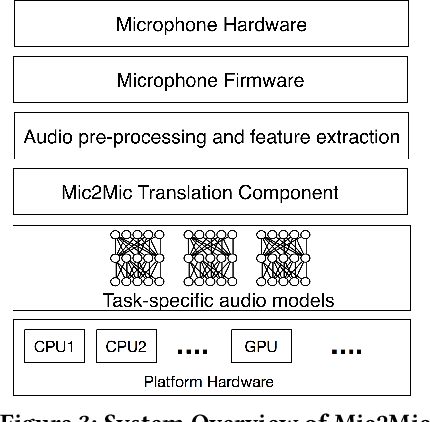
Mobile and embedded devices are increasingly using microphones and audio-based computational models to infer user context. A major challenge in building systems that combine audio models with commodity microphones is to guarantee their accuracy and robustness in the real-world. Besides many environmental dynamics, a primary factor that impacts the robustness of audio models is microphone variability. In this work, we propose Mic2Mic -- a machine-learned system component -- which resides in the inference pipeline of audio models and at real-time reduces the variability in audio data caused by microphone-specific factors. Two key considerations for the design of Mic2Mic were: a) to decouple the problem of microphone variability from the audio task, and b) put a minimal burden on end-users to provide training data. With these in mind, we apply the principles of cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks (CycleGANs) to learn Mic2Mic using unlabeled and unpaired data collected from different microphones. Our experiments show that Mic2Mic can recover between 66% to 89% of the accuracy lost due to microphone variability for two common audio tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge