Metamorphic Testing-based Adversarial Attack to Fool Deepfake Detectors
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2022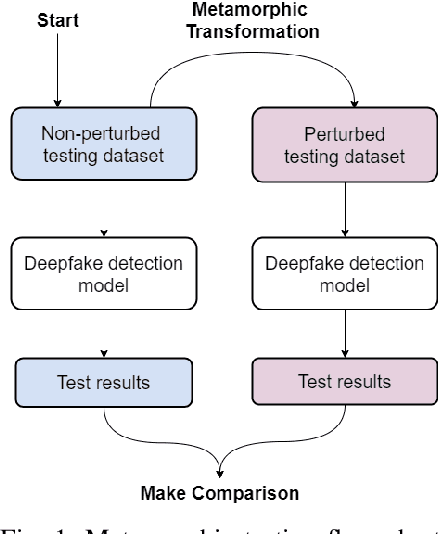
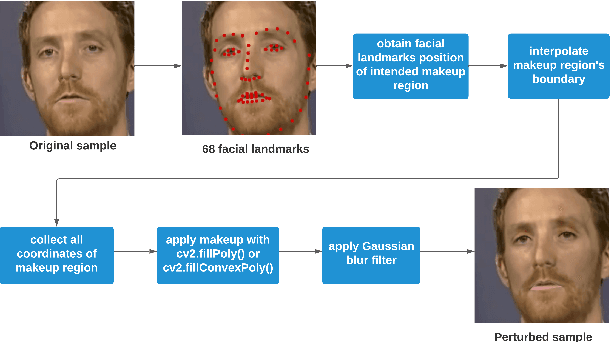
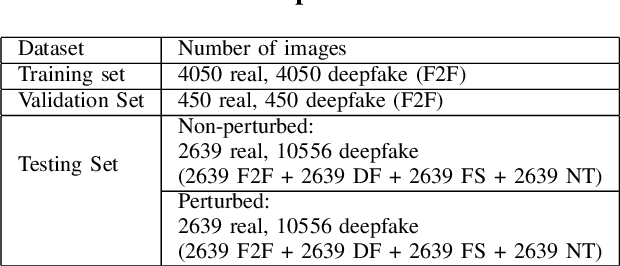
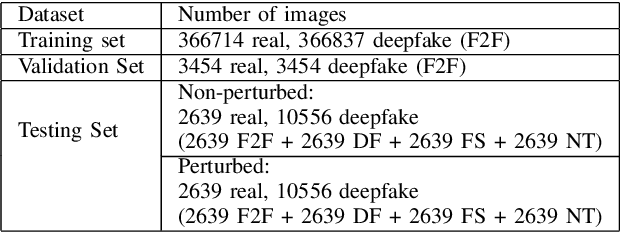
Deepfakes utilise Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques to create synthetic media where the likeness of one person is replaced with another. There are growing concerns that deepfakes can be maliciously used to create misleading and harmful digital contents. As deepfakes become more common, there is a dire need for deepfake detection technology to help spot deepfake media. Present deepfake detection models are able to achieve outstanding accuracy (>90%). However, most of them are limited to within-dataset scenario, where the same dataset is used for training and testing. Most models do not generalise well enough in cross-dataset scenario, where models are tested on unseen datasets from another source. Furthermore, state-of-the-art deepfake detection models rely on neural network-based classification models that are known to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Motivated by the need for a robust deepfake detection model, this study adapts metamorphic testing (MT) principles to help identify potential factors that could influence the robustness of the examined model, while overcoming the test oracle problem in this domain. Metamorphic testing is specifically chosen as the testing technique as it fits our demand to address learning-based system testing with probabilistic outcomes from largely black-box components, based on potentially large input domains. We performed our evaluations on MesoInception-4 and TwoStreamNet models, which are the state-of-the-art deepfake detection models. This study identified makeup application as an adversarial attack that could fool deepfake detectors. Our experimental results demonstrate that both the MesoInception-4 and TwoStreamNet models degrade in their performance by up to 30\% when the input data is perturbed with makeup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge