Memory Augmented Generative Adversarial Networks for Anomaly Detection
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2020
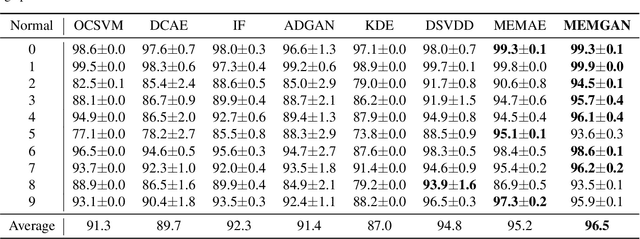
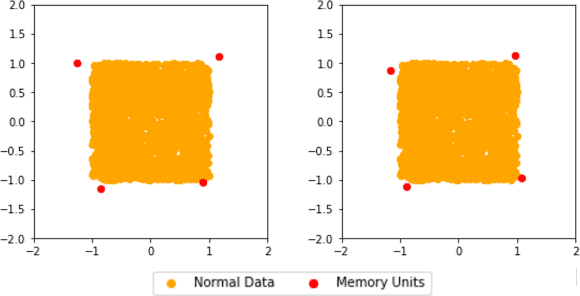
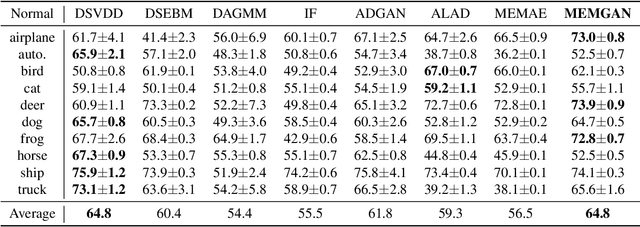
In this paper, we present a memory-augmented algorithm for anomaly detection. Classical anomaly detection algorithms focus on learning to model and generate normal data, but typically guarantees for detecting anomalous data are weak. The proposed Memory Augmented Generative Adversarial Networks (MEMGAN) interacts with a memory module for both the encoding and generation processes. Our algorithm is such that most of the \textit{encoded} normal data are inside the convex hull of the memory units, while the abnormal data are isolated outside. Such a remarkable property leads to good (resp.\ poor) reconstruction for normal (resp.\ abnormal) data and therefore provides a strong guarantee for anomaly detection. Decoded memory units in MEMGAN are more interpretable and disentangled than previous methods, which further demonstrates the effectiveness of the memory mechanism. Experimental results on twenty anomaly detection datasets of CIFAR-10 and MNIST show that MEMGAN demonstrates significant improvements over previous anomaly detection methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge