MELD: Meta-Reinforcement Learning from Images via Latent State Models
Paper and Code
Oct 26, 2020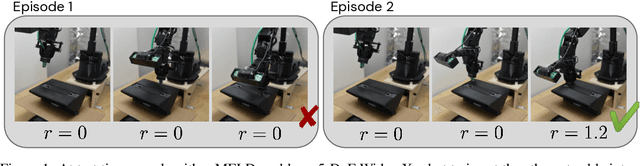
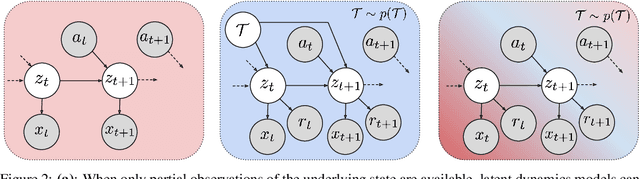
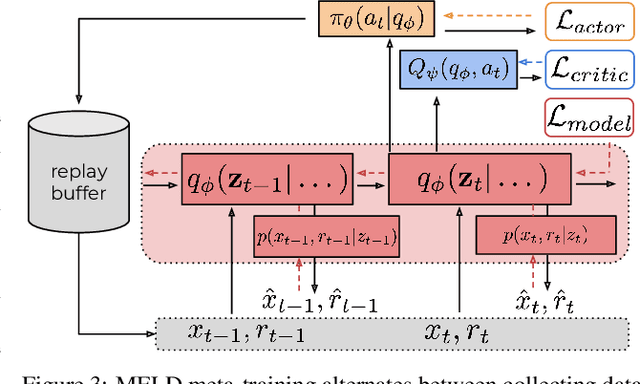
Meta-reinforcement learning algorithms can enable autonomous agents, such as robots, to quickly acquire new behaviors by leveraging prior experience in a set of related training tasks. However, the onerous data requirements of meta-training compounded with the challenge of learning from sensory inputs such as images have made meta-RL challenging to apply to real robotic systems. Latent state models, which learn compact state representations from a sequence of observations, can accelerate representation learning from visual inputs. In this paper, we leverage the perspective of meta-learning as task inference to show that latent state models can \emph{also} perform meta-learning given an appropriately defined observation space. Building on this insight, we develop meta-RL with latent dynamics (MELD), an algorithm for meta-RL from images that performs inference in a latent state model to quickly acquire new skills given observations and rewards. MELD outperforms prior meta-RL methods on several simulated image-based robotic control problems, and enables a real WidowX robotic arm to insert an Ethernet cable into new locations given a sparse task completion signal after only $8$ hours of real world meta-training. To our knowledge, MELD is the first meta-RL algorithm trained in a real-world robotic control setting from images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge