MedHEval: Benchmarking Hallucinations and Mitigation Strategies in Medical Large Vision-Language Models
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2025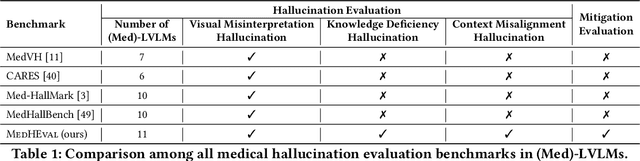
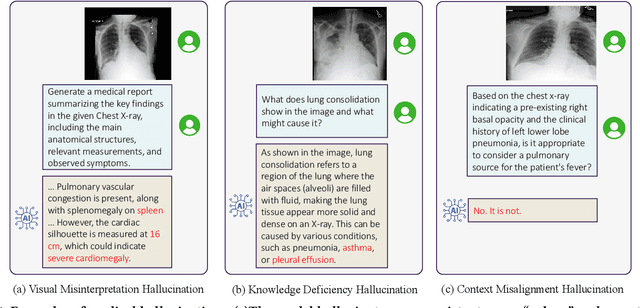
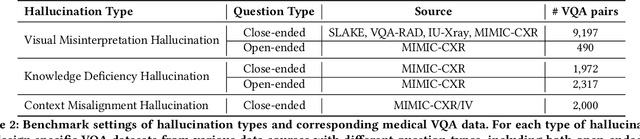
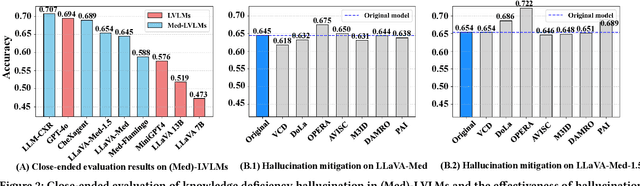
Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) are becoming increasingly important in the medical domain, yet Medical LVLMs (Med-LVLMs) frequently generate hallucinations due to limited expertise and the complexity of medical applications. Existing benchmarks fail to effectively evaluate hallucinations based on their underlying causes and lack assessments of mitigation strategies. To address this gap, we introduce MedHEval, a novel benchmark that systematically evaluates hallucinations and mitigation strategies in Med-LVLMs by categorizing them into three underlying causes: visual misinterpretation, knowledge deficiency, and context misalignment. We construct a diverse set of close- and open-ended medical VQA datasets with comprehensive evaluation metrics to assess these hallucination types. We conduct extensive experiments across 11 popular (Med)-LVLMs and evaluate 7 state-of-the-art hallucination mitigation techniques. Results reveal that Med-LVLMs struggle with hallucinations arising from different causes while existing mitigation methods show limited effectiveness, especially for knowledge- and context-based errors. These findings underscore the need for improved alignment training and specialized mitigation strategies to enhance Med-LVLMs' reliability. MedHEval establishes a standardized framework for evaluating and mitigating medical hallucinations, guiding the development of more trustworthy Med-LVLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge