MCBlock: Boosting Neural Radiance Field Training Speed by MCTS-based Dynamic-Resolution Ray Sampling
Paper and Code
Apr 14, 2025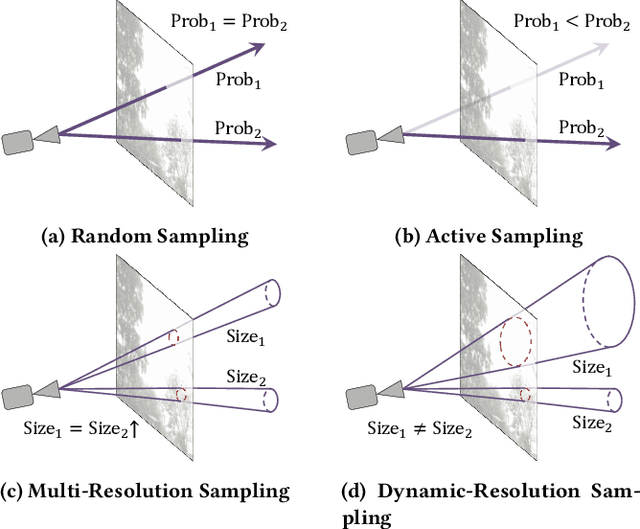
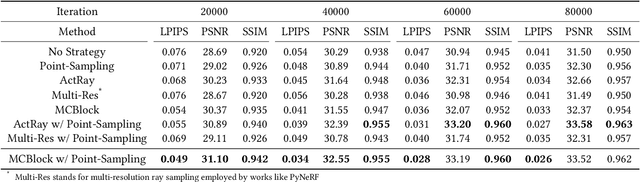
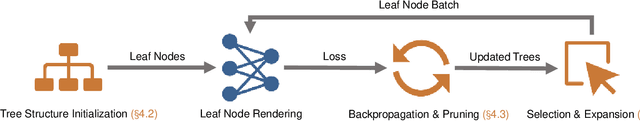
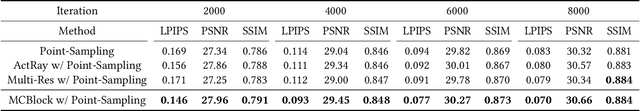
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) is widely known for high-fidelity novel view synthesis. However, even the state-of-the-art NeRF model, Gaussian Splatting, requires minutes for training, far from the real-time performance required by multimedia scenarios like telemedicine. One of the obstacles is its inefficient sampling, which is only partially addressed by existing works. Existing point-sampling algorithms uniformly sample simple-texture regions (easy to fit) and complex-texture regions (hard to fit), while existing ray-sampling algorithms sample these regions all in the finest granularity (i.e. the pixel level), both wasting GPU training resources. Actually, regions with different texture intensities require different sampling granularities. To this end, we propose a novel dynamic-resolution ray-sampling algorithm, MCBlock, which employs Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to partition each training image into pixel blocks with different sizes for active block-wise training. Specifically, the trees are initialized according to the texture of training images to boost the initialization speed, and an expansion/pruning module dynamically optimizes the block partition. MCBlock is implemented in Nerfstudio, an open-source toolset, and achieves a training acceleration of up to 2.33x, surpassing other ray-sampling algorithms. We believe MCBlock can apply to any cone-tracing NeRF model and contribute to the multimedia community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge