Maximally Permissive Reward Machines
Paper and Code
Aug 15, 2024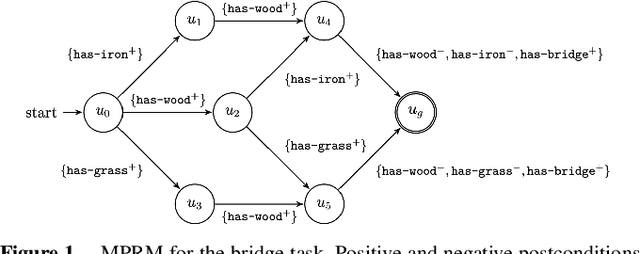
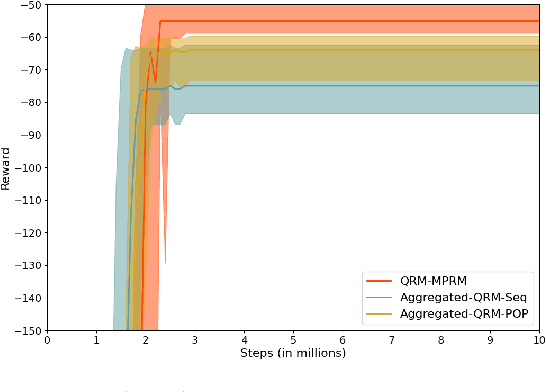
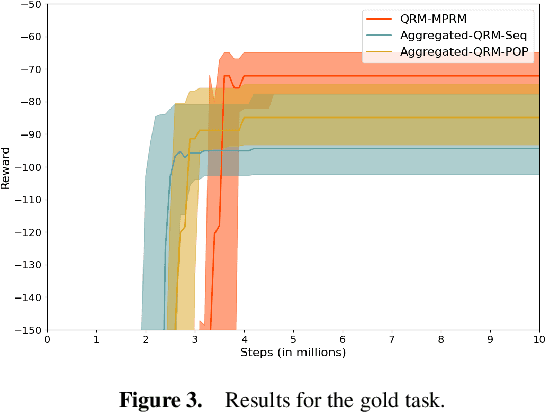
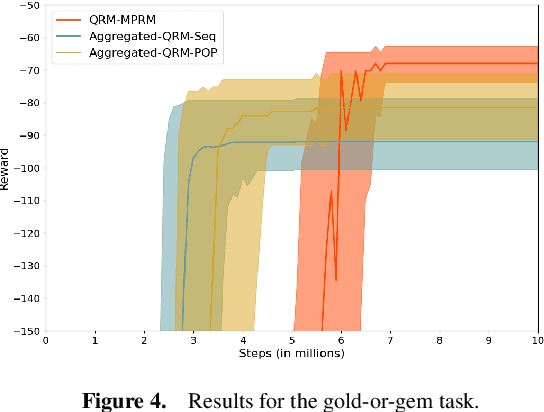
Reward machines allow the definition of rewards for temporally extended tasks and behaviors. Specifying "informative" reward machines can be challenging. One way to address this is to generate reward machines from a high-level abstract description of the learning environment, using techniques such as AI planning. However, previous planning-based approaches generate a reward machine based on a single (sequential or partial-order) plan, and do not allow maximum flexibility to the learning agent. In this paper we propose a new approach to synthesising reward machines which is based on the set of partial order plans for a goal. We prove that learning using such "maximally permissive" reward machines results in higher rewards than learning using RMs based on a single plan. We present experimental results which support our theoretical claims by showing that our approach obtains higher rewards than the single-plan approach in practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge