Maximally Compact and Separated Features with Regular Polytope Networks
Paper and Code
Jan 15, 2023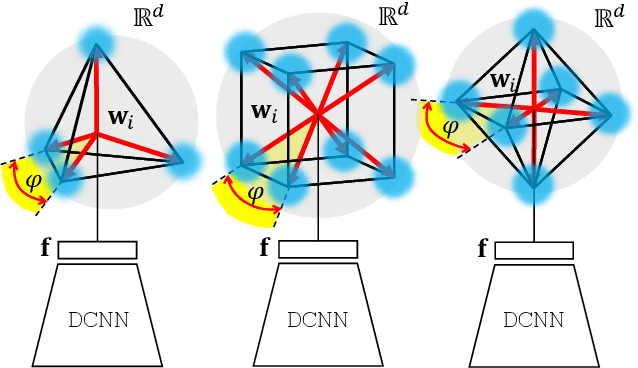
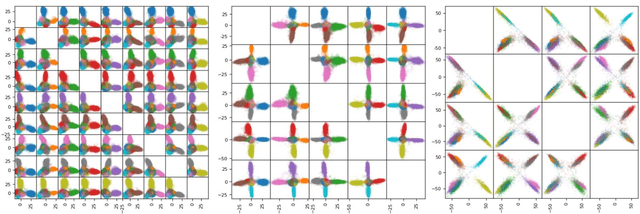
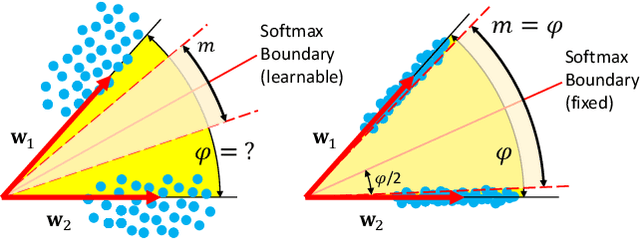
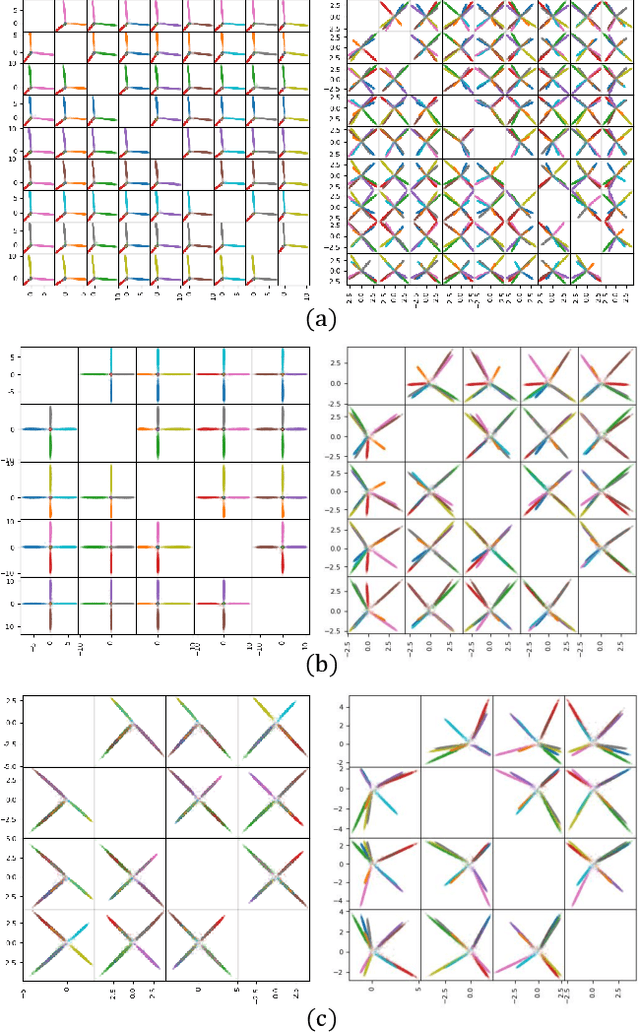
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained with the Softmax loss are widely used classification models for several vision tasks. Typically, a learnable transformation (i.e. the classifier) is placed at the end of such models returning class scores that are further normalized into probabilities by Softmax. This learnable transformation has a fundamental role in determining the network internal feature representation. In this work we show how to extract from CNNs features with the properties of \emph{maximum} inter-class separability and \emph{maximum} intra-class compactness by setting the parameters of the classifier transformation as not trainable (i.e. fixed). We obtain features similar to what can be obtained with the well-known ``Center Loss'' \cite{wen2016discriminative} and other similar approaches but with several practical advantages including maximal exploitation of the available feature space representation, reduction in the number of network parameters, no need to use other auxiliary losses besides the Softmax. Our approach unifies and generalizes into a common approach two apparently different classes of methods regarding: discriminative features, pioneered by the Center Loss \cite{wen2016discriminative} and fixed classifiers, firstly evaluated in \cite{hoffer2018fix}. Preliminary qualitative experimental results provide some insight on the potentialities of our combined strategy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge