$\mathsf{CSMAE~}$:~Cataract Surgical Masked Autoencoder (MAE) based Pre-training
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2025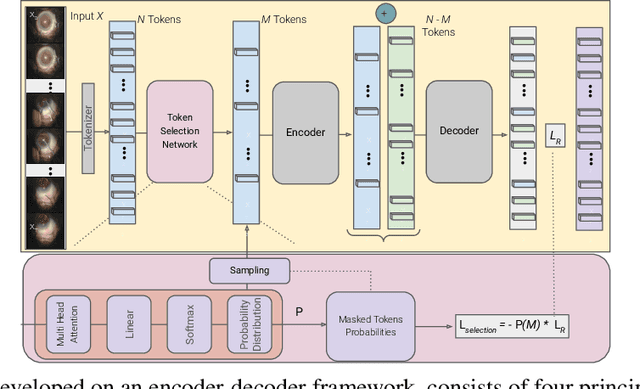
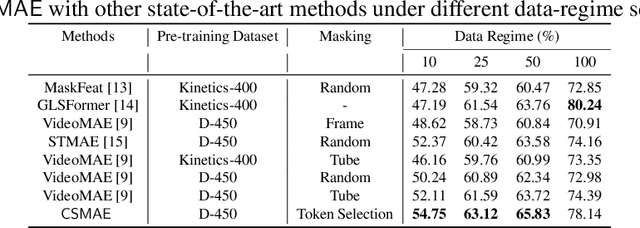

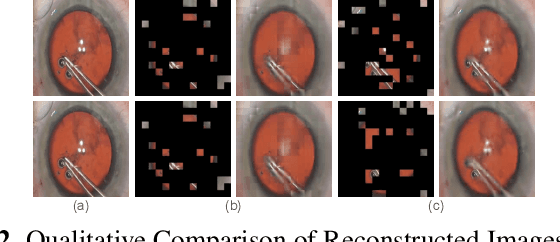
Automated analysis of surgical videos is crucial for improving surgical training, workflow optimization, and postoperative assessment. We introduce a CSMAE, Masked Autoencoder (MAE)-based pretraining approach, specifically developed for Cataract Surgery video analysis, where instead of randomly selecting tokens for masking, they are selected based on the spatiotemporal importance of the token. We created a large dataset of cataract surgery videos to improve the model's learning efficiency and expand its robustness in low-data regimes. Our pre-trained model can be easily adapted for specific downstream tasks via fine-tuning, serving as a robust backbone for further analysis. Through rigorous testing on a downstream step-recognition task on two Cataract Surgery video datasets, D99 and Cataract-101, our approach surpasses current state-of-the-art self-supervised pretraining and adapter-based transfer learning methods by a significant margin. This advancement not only demonstrates the potential of our MAE-based pretraining in the field of surgical video analysis but also sets a new benchmark for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge