Matern Gaussian processes on Riemannian manifolds
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2020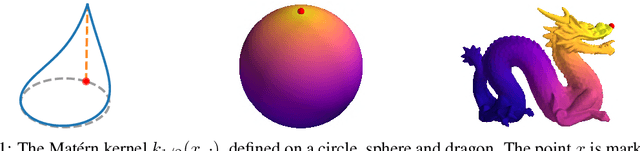
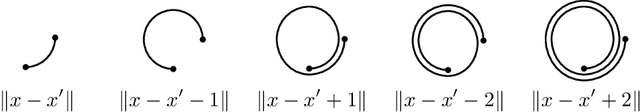

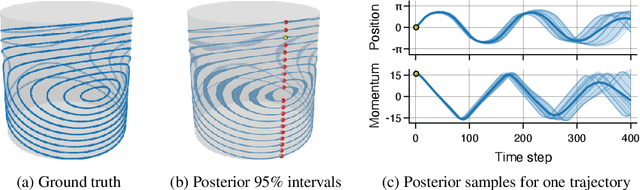
Gaussian processes are an effective model class for learning unknown functions, particularly in settings where accurately representing predictive uncertainty is of key importance. Motivated by applications in the physical sciences, the widely-used Mat\'{e}rn class of Gaussian processes has recently been generalized to model functions whose domains are Riemannian manifolds, by re-expressing said processes as solutions of stochastic partial differential equations. In this work, we propose techniques for computing the kernels of these processes via spectral theory of the Laplace--Beltrami operator in a fully constructive manner, thereby allowing them to be trained via standard scalable techniques such as inducing point methods. We also extend the generalization from the Mat\'{e}rn to the widely-used squared exponential Gaussian process. By allowing Riemannian Mat\'{e}rn Gaussian processes to be trained using well-understood techniques, our work enables their use in mini-batch, online, and non-conjugate settings, and makes them more accessible to machine learning practitioners.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge