Matching Questions and Answers in Dialogues from Online Forums
Paper and Code
May 19, 2020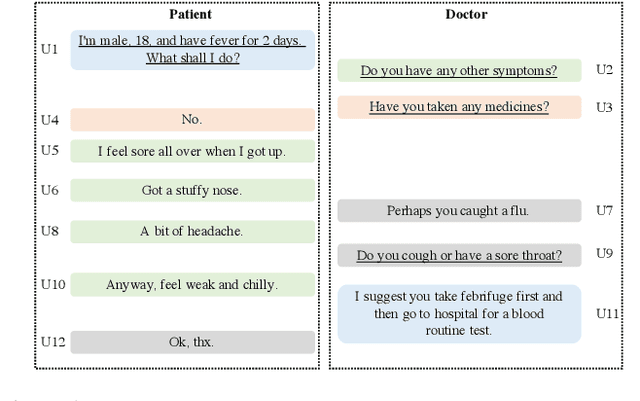

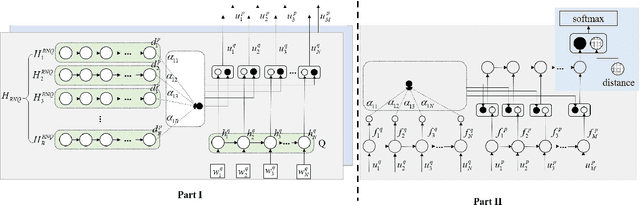

Matching question-answer relations between two turns in conversations is not only the first step in analyzing dialogue structures, but also valuable for training dialogue systems. This paper presents a QA matching model considering both distance information and dialogue history by two simultaneous attention mechanisms called mutual attention. Given scores computed by the trained model between each non-question turn with its candidate questions, a greedy matching strategy is used for final predictions. Because existing dialogue datasets such as the Ubuntu dataset are not suitable for the QA matching task, we further create a dataset with 1,000 labeled dialogues and demonstrate that our proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art and other strong baselines, particularly for matching long-distance QA pairs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge