Machine Unlearning in Forgettability Sequence
Paper and Code
Oct 09, 2024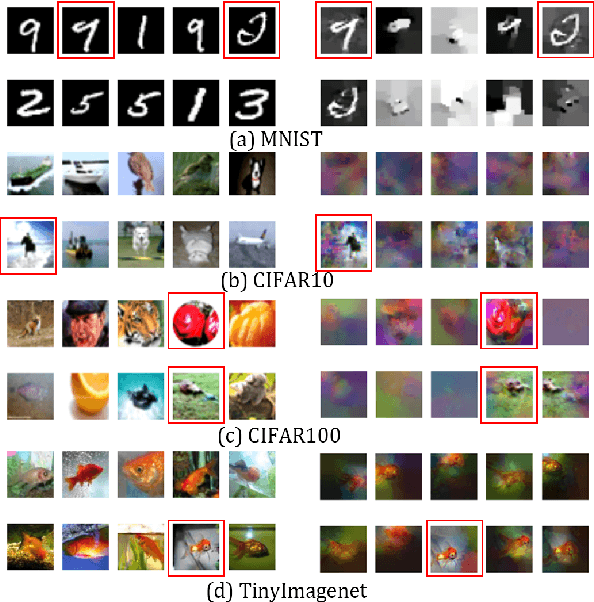
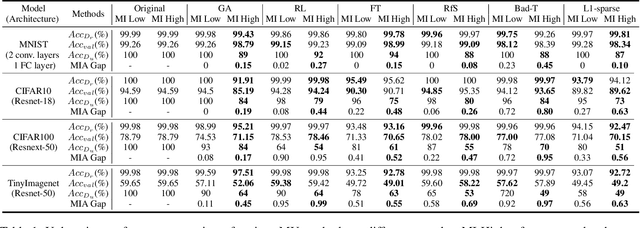
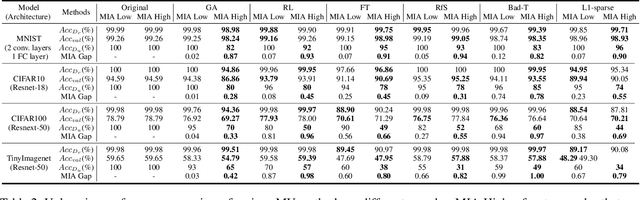
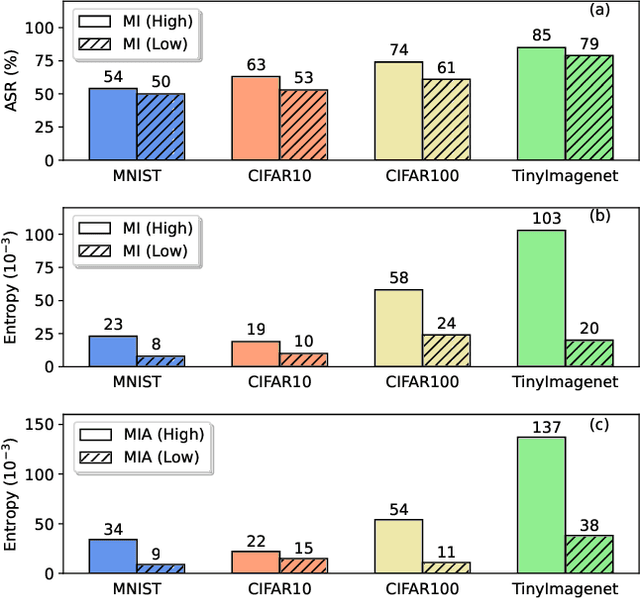
Machine unlearning (MU) is becoming a promising paradigm to achieve the "right to be forgotten", where the training trace of any chosen data points could be eliminated, while maintaining the model utility on general testing samples after unlearning. With the advancement of forgetting research, many fundamental open questions remain unanswered: do different samples exhibit varying levels of difficulty in being forgotten? Further, does the sequence in which samples are forgotten, determined by their respective difficulty levels, influence the performance of forgetting algorithms? In this paper, we identify key factor affecting unlearning difficulty and the performance of unlearning algorithms. We find that samples with higher privacy risks are more likely to be unlearning, indicating that the unlearning difficulty varies among different samples which motives a more precise unlearning mode. Built upon this insight, we propose a general unlearning framework, dubbed RSU, which consists of Ranking module and SeqUnlearn module.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge